
Cephalization is a characteristic mainly associated with which of the following types of body symmetry in animals?
a) Asymmetric
b) Radical
c) Biradial
d) Bilateral
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The body of the animals shows symmetry in the organization. The body plan can be divided into the radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and asymmetrical. Only sponges have asymmetry present in them which means they are not symmetrical in their body plans.
Complete answer:
The evolution from the cephalization occurred in the flatworms. In this, the head region was formed with the presence of the sense organs, mouth, nerve ganglia. Over many generations, it led to the formation of a distinct head region of the organism. This was then associated with the bilateral symmetry. It was the first step in the evolution of the head region.
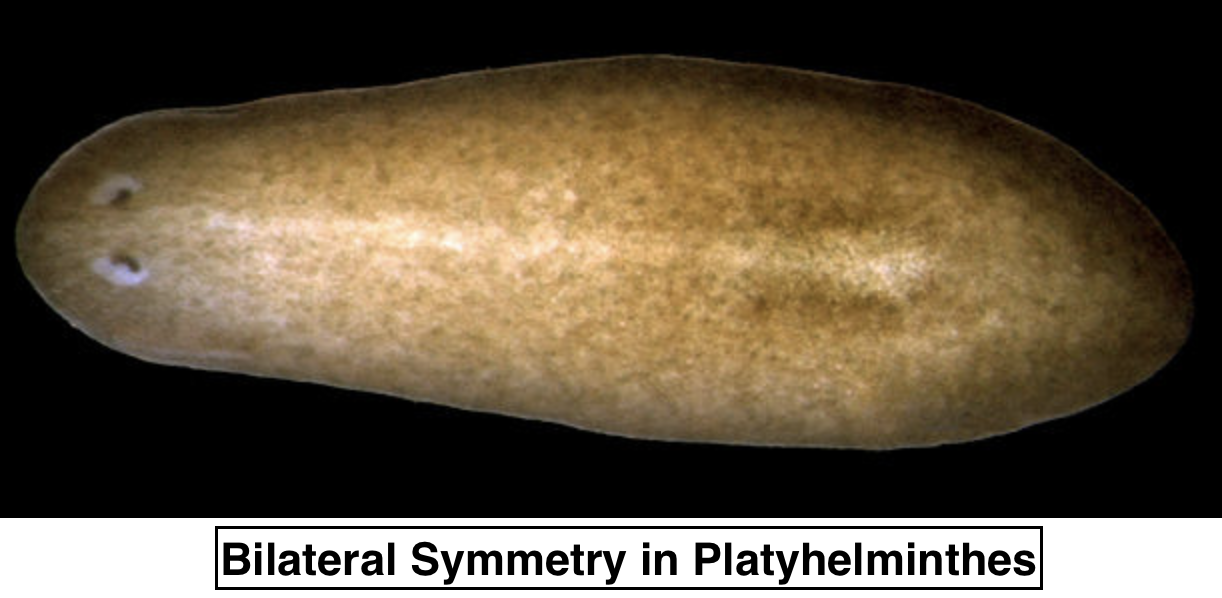
Due to the presence of the head region the animal was easily divided into two equal halves where the left part was identical to the right part. This symmetry helped the organism to have controlled movements in a particular direction.
Additional information: Radial symmetry occurs when the body can be divided into the upper and lower half or can be divided in the form of sun rays. There is no identical part in this symmetry. This is usually found in the cnidarians and Ctenophora. This symmetry helps the organism to move at a very slow pace. Bilateral symmetry is when the body of the organism can be divided into two identical parts. This symmetry helps the organism to move fast around in a particular direction.
So, the answer is ‘d) Bilateral symmetry’.
Note: The bilateral symmetry was formed in the organism due to the evolution that took place. The organisms earlier present didn’t have a distinct head region. The accumulation of the nerves in the head region leads to the formation of a distinct head in the organism.
Complete answer:
The evolution from the cephalization occurred in the flatworms. In this, the head region was formed with the presence of the sense organs, mouth, nerve ganglia. Over many generations, it led to the formation of a distinct head region of the organism. This was then associated with the bilateral symmetry. It was the first step in the evolution of the head region.

Due to the presence of the head region the animal was easily divided into two equal halves where the left part was identical to the right part. This symmetry helped the organism to have controlled movements in a particular direction.
Additional information: Radial symmetry occurs when the body can be divided into the upper and lower half or can be divided in the form of sun rays. There is no identical part in this symmetry. This is usually found in the cnidarians and Ctenophora. This symmetry helps the organism to move at a very slow pace. Bilateral symmetry is when the body of the organism can be divided into two identical parts. This symmetry helps the organism to move fast around in a particular direction.
So, the answer is ‘d) Bilateral symmetry’.
Note: The bilateral symmetry was formed in the organism due to the evolution that took place. The organisms earlier present didn’t have a distinct head region. The accumulation of the nerves in the head region leads to the formation of a distinct head in the organism.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




