
Cell recognition and adhesion are facilitated by components of plasma membranes. These components are generally
A. Protein molecules alone
B. Lipids alone
C. Both lipids and proteins
D. Glycolipids and Glycoproteins
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Like all the other cellular membranes the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The plasma membrane structure is a phospholipid bilayer which acts as a barrier between two aqueous compartments. Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and they carry out specific cell-cell recognition.
Complete answer:
Protein molecule alone- The molecular recognition is very crucial for singling, recognition, and catalysis. They all have different sizes and shapes these shapes determine the interaction of the molecules and protein interaction alone can’t recognize.
-Lipids are responsible for preserving the functional integrity of proteins. They interact between the phospholipid head group and hydrophobic portions of the protein.
-Both lipids and proteins are the main constituents of many biological membranes. They determine the basic structure of membranes. Membrane proteins are responsible for electrostatic and hydrophobic non-covalent interactions.
-Glycolipids and glycoproteins are distributed on the outer surface of the plasma membrane which is responsible for cell recognition and adhesion on the plasma membrane.
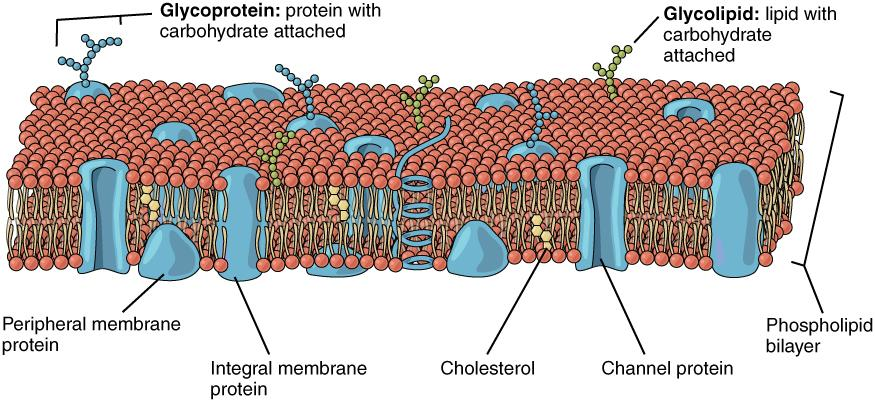
Hence, the answer is option D, Glycolipids, and Glycoproteins.
Note: Plasma membranes of animal cells contain asymmetrically distributed glycoproteins and glycolipids which will extend their carbohydrate portions to the extracellular environment which is very important in cell recognition. But in the cell membranes of fungi, bacteria, and higher plants they are in contact with a complex carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall will shield the underlying membranes in which they are in direct contact with the surroundings.
Complete answer:
Protein molecule alone- The molecular recognition is very crucial for singling, recognition, and catalysis. They all have different sizes and shapes these shapes determine the interaction of the molecules and protein interaction alone can’t recognize.
-Lipids are responsible for preserving the functional integrity of proteins. They interact between the phospholipid head group and hydrophobic portions of the protein.
-Both lipids and proteins are the main constituents of many biological membranes. They determine the basic structure of membranes. Membrane proteins are responsible for electrostatic and hydrophobic non-covalent interactions.
-Glycolipids and glycoproteins are distributed on the outer surface of the plasma membrane which is responsible for cell recognition and adhesion on the plasma membrane.

Hence, the answer is option D, Glycolipids, and Glycoproteins.
Note: Plasma membranes of animal cells contain asymmetrically distributed glycoproteins and glycolipids which will extend their carbohydrate portions to the extracellular environment which is very important in cell recognition. But in the cell membranes of fungi, bacteria, and higher plants they are in contact with a complex carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall will shield the underlying membranes in which they are in direct contact with the surroundings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




