
What is the Cartesian sign convention used for spherical mirrors?

Answer
617.7k+ views
- Hint- Here, we will be drawing the sign diagram which will represent the sign according to the object’s position. Based on this sign diagram all the signs of the important parameters like radius of curvature, focal length, etc are determined.
Complete step-by-step solution -
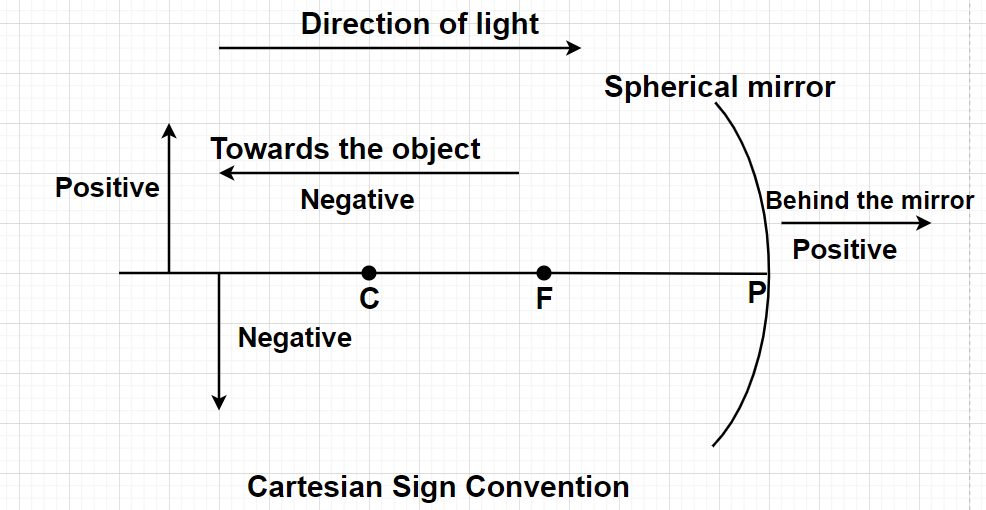
Cartesian sign convention in case of concave mirror:
$1.$ Since, the object is always placed in front of the mirror hence object distance is taken as negative.
$2.$ Since, the centre of curvature C and focus F lie in front of the concave mirror, so radius of curvature and focal length are taken as negative in the case of concave mirror.
$3.$ When an image is formed in front of the mirror, the distance of image is taken as negative and when image is formed behind the mirror, the distance of image is taken as positive.
$4.$ Height of image is taken as positive in the case of erect image and taken as negative in the case of inverted image.
Cartesian sign convention in case of convex mirror:
$1.$ Since, the object is always placed in front of the mirror hence object distance is taken as negative.
$2.$ Since, the centre of curvature C and focus F lies behind the convex mirror, so radius of curvature and focal length are taken as positive in the case of convex mirror.
$3.$ In the case of a convex mirror, the image is always formed behind the mirror, thus the distance of image is taken as positive.
$4.$ In the case of a convex mirror, always an erect image is formed, thus the height of the image is taken as positive always.
Note- The focal point is defined as the point at which incoming light rays that are parallel to the principal axis would meet after reflection and the focal length is the perpendicular distance from the centre of the mirror to the focal point. The radius of curvature is defined as the radius of the sphere that would be produced if the mirror was made into a full sphere.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Cartesian sign convention in case of concave mirror:
$1.$ Since, the object is always placed in front of the mirror hence object distance is taken as negative.
$2.$ Since, the centre of curvature C and focus F lie in front of the concave mirror, so radius of curvature and focal length are taken as negative in the case of concave mirror.
$3.$ When an image is formed in front of the mirror, the distance of image is taken as negative and when image is formed behind the mirror, the distance of image is taken as positive.
$4.$ Height of image is taken as positive in the case of erect image and taken as negative in the case of inverted image.
Cartesian sign convention in case of convex mirror:
$1.$ Since, the object is always placed in front of the mirror hence object distance is taken as negative.
$2.$ Since, the centre of curvature C and focus F lies behind the convex mirror, so radius of curvature and focal length are taken as positive in the case of convex mirror.
$3.$ In the case of a convex mirror, the image is always formed behind the mirror, thus the distance of image is taken as positive.
$4.$ In the case of a convex mirror, always an erect image is formed, thus the height of the image is taken as positive always.
Note- The focal point is defined as the point at which incoming light rays that are parallel to the principal axis would meet after reflection and the focal length is the perpendicular distance from the centre of the mirror to the focal point. The radius of curvature is defined as the radius of the sphere that would be produced if the mirror was made into a full sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




