
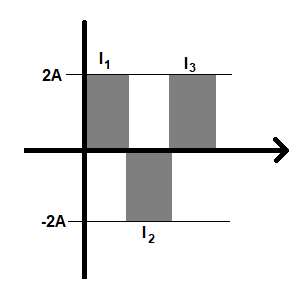
Calculate the rms value of A.C. as shown in the figure.

Answer
603k+ views
Hint: The full form of rms value is root mean square value. The meaning of root mean square is the square root of the mean of the squares of the given values. It is an alternative for mean value of given numbers. Sometimes, it is more useful than mean value.
Complete step by step answer:
Sometimes when we find the mean (average) value of the values of an oscillating function, we get the mean value as zero. This is because the function has both positive as well as negative values and the sum is zero, making the value of mean zero. However, zero signifies nothing and we do not want that.
For example, take an alternating current that is a sinusoidal function of time, $i={{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t)$. The mean value of a sine function for an interval of $2\pi $is zero. However, this value cannot help us to understand the circuit.
Due to this reason, we have an alternative way for an average value of multiple values and that is root mean square value (rms value).
Rms value of a function is the root mean square value. It is the square root of the mean of the squares of the numbers. It is always positive.
Let us calculate the root mean square value for the given data.
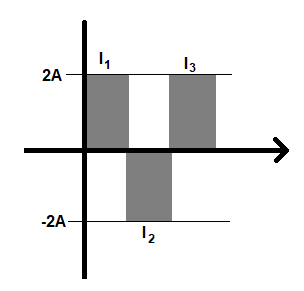
There are three values of current, ${{I}_{1}}$, ${{I}_{2}}$ and ${{I}_{3}}$. If we look at the figure, the values of ${{I}_{1}}$, ${{I}_{2}}$ and ${{I}_{3}}$ are 2A, -2A and 2A. The rms value of this values will be ${{I}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{I}_{1}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}}{3}}$.
First, let us calculate the mean of the squares (${{I}^{2}}_{mean}$) of the three current values. For the mean of squares, calculate the sum of the squares of the three currents and divide the sum by 3 since there are three currents.
Therefore, $\begin{align}
& {{I}^{2}}_{mean}=\dfrac{{{I}_{1}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}}{3} \\
& \text{ }=\dfrac{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}}{3}=\dfrac{4+4+4}{3}=\dfrac{12}{3}=4 \\
\end{align}$
The root mean value will be ${{I}_{rms}}=\sqrt{{{I}^{2}}_{mean}}=\sqrt{4}=2$
Therefore, the rms value of the three given current values is 2A.
Note: In this problem, there were only three current values. Sometimes there are infinite values in a function e.g. $i={{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t)$. If you take an interval of time in this function, the root mean square value for this interval cannot be calculated by a simple summation. Here, we have to integrate the function with time for the given interval i.e. $\int{i.dt=}\int{{{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t).dt}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Sometimes when we find the mean (average) value of the values of an oscillating function, we get the mean value as zero. This is because the function has both positive as well as negative values and the sum is zero, making the value of mean zero. However, zero signifies nothing and we do not want that.
For example, take an alternating current that is a sinusoidal function of time, $i={{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t)$. The mean value of a sine function for an interval of $2\pi $is zero. However, this value cannot help us to understand the circuit.
Due to this reason, we have an alternative way for an average value of multiple values and that is root mean square value (rms value).
Rms value of a function is the root mean square value. It is the square root of the mean of the squares of the numbers. It is always positive.
Let us calculate the root mean square value for the given data.

There are three values of current, ${{I}_{1}}$, ${{I}_{2}}$ and ${{I}_{3}}$. If we look at the figure, the values of ${{I}_{1}}$, ${{I}_{2}}$ and ${{I}_{3}}$ are 2A, -2A and 2A. The rms value of this values will be ${{I}_{rms}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{I}_{1}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}}{3}}$.
First, let us calculate the mean of the squares (${{I}^{2}}_{mean}$) of the three current values. For the mean of squares, calculate the sum of the squares of the three currents and divide the sum by 3 since there are three currents.
Therefore, $\begin{align}
& {{I}^{2}}_{mean}=\dfrac{{{I}_{1}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}+{{I}_{3}}^{2}}{3} \\
& \text{ }=\dfrac{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}}{3}=\dfrac{4+4+4}{3}=\dfrac{12}{3}=4 \\
\end{align}$
The root mean value will be ${{I}_{rms}}=\sqrt{{{I}^{2}}_{mean}}=\sqrt{4}=2$
Therefore, the rms value of the three given current values is 2A.
Note: In this problem, there were only three current values. Sometimes there are infinite values in a function e.g. $i={{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t)$. If you take an interval of time in this function, the root mean square value for this interval cannot be calculated by a simple summation. Here, we have to integrate the function with time for the given interval i.e. $\int{i.dt=}\int{{{i}_{\circ }}\sin (\omega t).dt}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




