
Calculate the resonance energy of ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$, using kekule formula for ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$ from the following data:
(i)- $\Delta {{H}^{\circ }}$ for ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$ = -358.5 KJ /mol.
(ii)- Heat of atomization of C = 716. 8 KJ /mol
(iii)- Bond energy of C-H, C-C, C=C, H-H are 490, 340, 620, and 436.9 KJ /mol.
Report your answer in KJ (only value).
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: To find the resonance energy of the benzene, we have to write the correct and balanced equation: $6C(s)+3{{H}_{2}}(g)\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$. The resonance energy is equal to the difference between the expected enthalpy and the calculated enthalpy.
Complete step-by-step answer:The given value of the enthalpy of the benzene, i.e., ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$ is -358.5 KJ /mol. This value can be written as expected enthalpy ($\Delta {{H}_{\exp }}$). To find the resonance energy, we have to find the calculated or observed enthalpy. For this, we have to write the correct and balanced reaction of the formation of benzene from carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
$6C(s)+3{{H}_{2}}(g)\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$
In structure form, it will be:
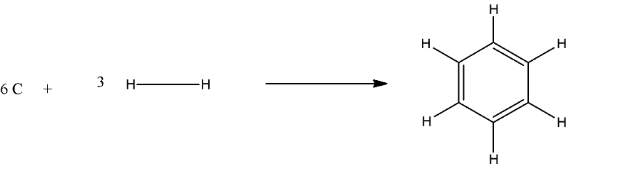
The calculated enthalpy will be equal to the difference of the enthalpy of the reactant and the enthalpy of the Product.
On the product side, the bond energy of C-H is 490 KJ /mol, C=C is 620 KJ /mol, and C-C is 340 KJ /mol. On the reactant side, the bond energy of H-H is 436.9 KJ /mol, and the heat of the atomization of carbon is 716.8 KJ /mol. We can calculate the enthalpy as:
$\Delta {{H}_{cal}}=[3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{H-H}}+6\text{ x }{{\text{H}}_{atom}}]-[3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C=C}}+3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C-C}}+6\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C-H}}]$
$\Rightarrow \Delta {{H}_{cal}}=[3\text{ x 436}\text{.9}+6\text{ x 716}\text{.8}]-[3\text{ x 620}+3\text{ x 340}+6\text{ x 490}]$
$\therefore \Delta {{H}_{cal}}=5611.5-5820=-208.5\text{ KJ /mol}$.
So, the calculated value is -208.5 KJ /mol.
The resonance energy will be = $\Delta {{H}_{\exp }}-\Delta {{H}_{cal}}$
Putting the values, we have:
$R.E=-358.5-(-208.5)=-150.0\text{ kJ}$
The resonance energy of the benzene is -150.0 kJ.
Note: It must be noted carefully that when you are calculating the enthalpy of the compound using the bond energies, the bond energy of the reactants must be written first then the bond energy of the products.
Complete step-by-step answer:The given value of the enthalpy of the benzene, i.e., ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$ is -358.5 KJ /mol. This value can be written as expected enthalpy ($\Delta {{H}_{\exp }}$). To find the resonance energy, we have to find the calculated or observed enthalpy. For this, we have to write the correct and balanced reaction of the formation of benzene from carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
$6C(s)+3{{H}_{2}}(g)\to {{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$
In structure form, it will be:

The calculated enthalpy will be equal to the difference of the enthalpy of the reactant and the enthalpy of the Product.
On the product side, the bond energy of C-H is 490 KJ /mol, C=C is 620 KJ /mol, and C-C is 340 KJ /mol. On the reactant side, the bond energy of H-H is 436.9 KJ /mol, and the heat of the atomization of carbon is 716.8 KJ /mol. We can calculate the enthalpy as:
$\Delta {{H}_{cal}}=[3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{H-H}}+6\text{ x }{{\text{H}}_{atom}}]-[3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C=C}}+3\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C-C}}+6\text{ x }{{\text{E}}_{C-H}}]$
$\Rightarrow \Delta {{H}_{cal}}=[3\text{ x 436}\text{.9}+6\text{ x 716}\text{.8}]-[3\text{ x 620}+3\text{ x 340}+6\text{ x 490}]$
$\therefore \Delta {{H}_{cal}}=5611.5-5820=-208.5\text{ KJ /mol}$.
So, the calculated value is -208.5 KJ /mol.
The resonance energy will be = $\Delta {{H}_{\exp }}-\Delta {{H}_{cal}}$
Putting the values, we have:
$R.E=-358.5-(-208.5)=-150.0\text{ kJ}$
The resonance energy of the benzene is -150.0 kJ.
Note: It must be noted carefully that when you are calculating the enthalpy of the compound using the bond energies, the bond energy of the reactants must be written first then the bond energy of the products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




