
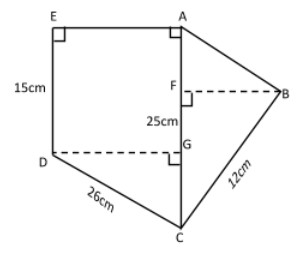
Calculate the area of the figure given below: which is not drawn to scale.
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{A.{\text{ }}630sq.cm} \\
{B.{\text{ }}620sq.cm} \\
{C.{\text{ }}640sq.cm} \\
{D.{\text{ }}600sq.cm}
\end{array}\]

Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Joint DG divides DCAE into two polygons via ΔGCD and AGDE.
Further find area of $\Delta ABC$ and area of $\Delta GCD$ and the area of rectangle AGDE.
Then add the areas of two triangles$(\Delta ABC\,and\,\Delta GCD)$and rectangle AGDE.
Area of triangle $ = \dfrac{{base \times height}}{2}$ and area of rectangle\[ = length \times breadth.\]
Complete step by step solution:
From D, draw perpendicular such that\[DG \bot AC\] ,thereby,
making a right angled triangle GCD and rectangle AGDE.
Given: \[AC = 25cm\]
\[AC = AG + GC\]
As, \[AG = ED\] (opposite sides of rectangle)
\[\therefore AC = ED + GC\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25\,\,{\text{ = }}15 + GC\] \[\left[ {As{\text{ }}ED\; = 15{\text{ }}cm} \right]\]
⇒ GC = 25 -15 = 10 cm \[ \ldots .\left( 1 \right)\]
In \[\Delta GCD;\]
By using Pythagoras theorem,
${(hypotenuse)^2} = {(perpendicular\,)^2} + {(base)^2}$
\[C{D^2} = G{C^2} + G{D^2}\]
Or\[{26^2} = {10^2} + G{D^2}\] \[\left[ {GC = 10{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 1 \right),CD = 26{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}given} \right]\]
\[G{D^2} = {26^2} - {10^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 676-100 = 576\]
$GD = \sqrt {576} $
\[GD = 24{\text{ }}cm\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \ldots .\left( 2 \right)\]
Entire figure consists of three parts viz;
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{\left( 1 \right)\Delta ABC} \\
{\left( 2 \right)\Delta GCD} \\
{\left( 3 \right)Rectangle{\text{ }}AGDE}
\end{array}\]
$\therefore ar(ABCDE) = ar(\Delta ABC) + ar(\Delta GCD) + ar(AGDE)$
\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 25 \times 12 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 24 + 15 \times 24\] \[\left[ {GC = 10{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 1 \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}GD = 24{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 2 \right)} \right]\]
$ = 150 + 120 + 360$
$ = 630sq\,cm$
Thus, the area of the given figure is\[630sq{\text{ }}cm\] .
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In$\Delta ABC$and $\Delta GCD$one angle is \[90^\circ \]so, these two triangles are right angled triangles, that is why we used the formula area of triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$.
Further find area of $\Delta ABC$ and area of $\Delta GCD$ and the area of rectangle AGDE.
Then add the areas of two triangles$(\Delta ABC\,and\,\Delta GCD)$and rectangle AGDE.
Area of triangle $ = \dfrac{{base \times height}}{2}$ and area of rectangle\[ = length \times breadth.\]
Complete step by step solution:
From D, draw perpendicular such that\[DG \bot AC\] ,thereby,
making a right angled triangle GCD and rectangle AGDE.
Given: \[AC = 25cm\]
\[AC = AG + GC\]
As, \[AG = ED\] (opposite sides of rectangle)
\[\therefore AC = ED + GC\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25\,\,{\text{ = }}15 + GC\] \[\left[ {As{\text{ }}ED\; = 15{\text{ }}cm} \right]\]
⇒ GC = 25 -15 = 10 cm \[ \ldots .\left( 1 \right)\]
In \[\Delta GCD;\]
By using Pythagoras theorem,
${(hypotenuse)^2} = {(perpendicular\,)^2} + {(base)^2}$
\[C{D^2} = G{C^2} + G{D^2}\]
Or\[{26^2} = {10^2} + G{D^2}\] \[\left[ {GC = 10{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 1 \right),CD = 26{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}given} \right]\]
\[G{D^2} = {26^2} - {10^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 676-100 = 576\]
$GD = \sqrt {576} $
\[GD = 24{\text{ }}cm\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \ldots .\left( 2 \right)\]
Entire figure consists of three parts viz;
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{\left( 1 \right)\Delta ABC} \\
{\left( 2 \right)\Delta GCD} \\
{\left( 3 \right)Rectangle{\text{ }}AGDE}
\end{array}\]
$\therefore ar(ABCDE) = ar(\Delta ABC) + ar(\Delta GCD) + ar(AGDE)$
\[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 25 \times 12 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 24 + 15 \times 24\] \[\left[ {GC = 10{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 1 \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}GD = 24{\text{ }}cm{\text{ }}from{\text{ }}\left( 2 \right)} \right]\]
$ = 150 + 120 + 360$
$ = 630sq\,cm$
Thus, the area of the given figure is\[630sq{\text{ }}cm\] .
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In$\Delta ABC$and $\Delta GCD$one angle is \[90^\circ \]so, these two triangles are right angled triangles, that is why we used the formula area of triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




