
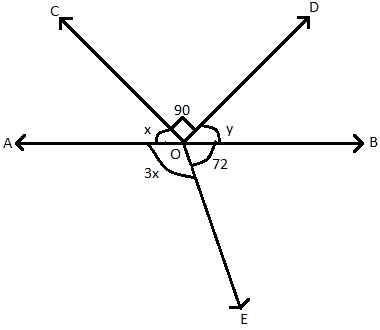
Calculate $\angle AOC,\angle BOD,\angle AOE$ in the figure given below, given that angle $\angle COD={{90}^{\circ }}$, $\angle BOE={{72}^{\circ }}$and AOB is a straight line. \[\]

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: We use the fact that the sum of angles subtended by ray on a straight line (called linear pair of angles or supplementary angles if the number of angles is 2 ) is $180{}^\circ$. We take the linear pair of angles $\angle AOE$ and $\angle BOE$ and solve $\angle AOE+\angle BOE={{180}^{\circ }}$ to get $\angle AOE=3x,\angle AOC=x$. Then we take linear triple of angles $\angle AOC+\angle BOD+\angle COD={{180}^{\circ }}$ to get $\angle BOD=y$\[\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know from geometry that the couple of angles that lie on a straight line on the same side are known as linear pair or supplementary angles , their sum is $180{}^\circ$. According to the question, line AOB is a straight line. So, the sum of the $\angle AOE$and $\angle BOE$ will be $180{}^\circ $ as they are linear pairs of angles subtended on a straight line by the ray $\overrightarrow{OE}$ . It is also given in the question that $\angle AOE=3x$ and $\angle BOE={{72}^{\circ }}$. So we have
\[\begin{align}
& \angle AOE+\angle BOE=\angle AOB={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 3x+{{72}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 3x={{180}^{\circ }}-{{72}^{\circ }}={{108}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{{{108}^{\circ }}}{3}={{36}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
So we obtained the measure of $\angle AOE$ as,
\[\angle AOE=3x=3\times {{36}^{\circ }}={{108}^{\circ }}\]
Now we observe the angles above the line AOB which are $\angle AOC,\angle BOD,\angle BOD.$ We are given in the question that $\angle AOC=x,\angle BOD={{90}^{\circ }},\angle BOD=y.$ These three angles are subtended on the straight line AOB by the rays $\overrightarrow{OC},\overrightarrow{OD}$. So their sum is also ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We have previously obtained $\angle AOC=x={{36}^{\circ }}.$ We use these values and have,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle AOC+\angle BOD+\angle BOD=\angle AOB \\
& \Rightarrow x+{{90}^{\circ }}+y={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow {{36}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}+y={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y={{180}^{\circ }}-{{126}^{\circ }}={{54}^{\circ }}=\angle BOD \\
\end{align}\]
So the measures of the required angle are $\angle AOC={{36}^{\circ }},\angle BOD={{54}^{\circ }},\angle AOE={{108}^{\circ }}$\[\]
Note: We must be careful of the confusion between linear pairs and opposite angles. Linear pairs are the couple of angles that lie on the same side of a straight line say $L$ when another line ${{L}^{'}}$ intersects $L$ whose sum is $180{}^\circ $ . Opposite angles are the couple of angles obtained at the opposite side of the line $L$ and they are equal in measurement.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know from geometry that the couple of angles that lie on a straight line on the same side are known as linear pair or supplementary angles , their sum is $180{}^\circ$. According to the question, line AOB is a straight line. So, the sum of the $\angle AOE$and $\angle BOE$ will be $180{}^\circ $ as they are linear pairs of angles subtended on a straight line by the ray $\overrightarrow{OE}$ . It is also given in the question that $\angle AOE=3x$ and $\angle BOE={{72}^{\circ }}$. So we have
\[\begin{align}
& \angle AOE+\angle BOE=\angle AOB={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 3x+{{72}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow 3x={{180}^{\circ }}-{{72}^{\circ }}={{108}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{{{108}^{\circ }}}{3}={{36}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
So we obtained the measure of $\angle AOE$ as,
\[\angle AOE=3x=3\times {{36}^{\circ }}={{108}^{\circ }}\]
Now we observe the angles above the line AOB which are $\angle AOC,\angle BOD,\angle BOD.$ We are given in the question that $\angle AOC=x,\angle BOD={{90}^{\circ }},\angle BOD=y.$ These three angles are subtended on the straight line AOB by the rays $\overrightarrow{OC},\overrightarrow{OD}$. So their sum is also ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We have previously obtained $\angle AOC=x={{36}^{\circ }}.$ We use these values and have,
\[\begin{align}
& \angle AOC+\angle BOD+\angle BOD=\angle AOB \\
& \Rightarrow x+{{90}^{\circ }}+y={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow {{36}^{\circ }}+{{90}^{\circ }}+y={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y={{180}^{\circ }}-{{126}^{\circ }}={{54}^{\circ }}=\angle BOD \\
\end{align}\]
So the measures of the required angle are $\angle AOC={{36}^{\circ }},\angle BOD={{54}^{\circ }},\angle AOE={{108}^{\circ }}$\[\]
Note: We must be careful of the confusion between linear pairs and opposite angles. Linear pairs are the couple of angles that lie on the same side of a straight line say $L$ when another line ${{L}^{'}}$ intersects $L$ whose sum is $180{}^\circ $ . Opposite angles are the couple of angles obtained at the opposite side of the line $L$ and they are equal in measurement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




