
$ {C_2}{H_2}\xrightarrow{{NaN{H_2}}}A\xrightarrow{{1 - Bromohep\tan e}}B $
What is B in the above reaction?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint :Sodium amide or sodamide ( $ NaN{H_2} $ ) is a strong base widely used in organic reactions. It is prepared by the reaction of sodium with ammonia gas. Sodium amide is similar to Lithium diisopropylamide ( $ LDA $ ).
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In the question it is given that acetylene reacts with sodamide to yield A which then further reacts with alkyl halide(1-Bromoheptane) to yield B. We have to find B.
Sodium amide $ \left( {NaN{H_2}} \right) $ is a strong base which can easily deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, ketones and other functional groups having acidic protons.
In this reaction, Sodium amide will deprotonate acetylene to yield acetylide ion (A) which further reacts with 1-Bromoheptane (alkyl halide) and undergo nucleophilic substitution to yield 1-nonyne (B).
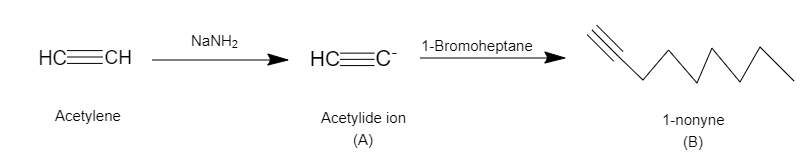
The terminal proton of acetylene is highly acidic and is very easily removed in the presence of sodium amide which is a strong base forming acetylide ion. Bromine is a good leaving group leading to nucleophilic substitution reaction. Also, acetylide ion is a good nucleophile forming 1-nonyne.
Additional Information:
Another important application of sodium amide is the formation of alkynes from geminal or vicinal dihalides. It should be noted that Sodium amide reacts violently with water to produce ammonia and sodium hydroxide hence should be handled with care.
Note :
In order to complete such reactions, we should be aware of the properties and nature of the reagent given. For example; in this question Sodium amide was given which is a good base and hence will abstract the acidic proton using this information we were able to complete the reaction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In the question it is given that acetylene reacts with sodamide to yield A which then further reacts with alkyl halide(1-Bromoheptane) to yield B. We have to find B.
Sodium amide $ \left( {NaN{H_2}} \right) $ is a strong base which can easily deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, ketones and other functional groups having acidic protons.
In this reaction, Sodium amide will deprotonate acetylene to yield acetylide ion (A) which further reacts with 1-Bromoheptane (alkyl halide) and undergo nucleophilic substitution to yield 1-nonyne (B).

The terminal proton of acetylene is highly acidic and is very easily removed in the presence of sodium amide which is a strong base forming acetylide ion. Bromine is a good leaving group leading to nucleophilic substitution reaction. Also, acetylide ion is a good nucleophile forming 1-nonyne.
Additional Information:
Another important application of sodium amide is the formation of alkynes from geminal or vicinal dihalides. It should be noted that Sodium amide reacts violently with water to produce ammonia and sodium hydroxide hence should be handled with care.
Note :
In order to complete such reactions, we should be aware of the properties and nature of the reagent given. For example; in this question Sodium amide was given which is a good base and hence will abstract the acidic proton using this information we were able to complete the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




