
What is budding? Explain the budding in Hydra by the help of diagrams.
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Budding is the process of production of new organisms. It is an asexual mode of reproduction. Examples of budding are yeast, hydra, corals, jellyfish, etc. It is associated with both unicellular and with multicellular organisms.
Complete answer:
>In budding, a new individual developed from a small part of the parent. A bud that is formed during budding detaches itself from the parent body and develops into a new organism. At the time of separation, a new individual leaves scar tissue behind them.
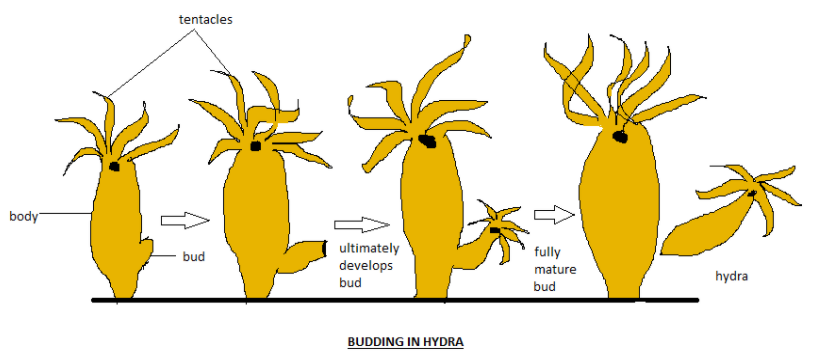
>Budding in hydra takes place by the regenerative cells in which bud extends as an outgrowth as shown in the diagram. These buds develop into a new organism which detaches them from the parent body at the time of maturation.
>Hydra is found in freshwater. It is small and has a tubular structure that is composed of tentacles. In hydra, budding involves a small bud which is developed from their parent hydra by the help of mitotic cell division.
>Small buds receive protein and nutrition from the parent hydra. They grow healthy and their growth starts by developing mouth and small tentacles. Finally, hydra separated from their parent body and became an independent organism.
Note:As budding is a type of asexual reproduction. So, a newly developed individual is a replica of their parents and they are genetically similar. Budding takes place in unicellular organisms as well as multicellular organisms. Both hydra and yeast can be reproduced by the help of budding.
Complete answer:
>In budding, a new individual developed from a small part of the parent. A bud that is formed during budding detaches itself from the parent body and develops into a new organism. At the time of separation, a new individual leaves scar tissue behind them.
>Budding in hydra takes place by the regenerative cells in which bud extends as an outgrowth as shown in the diagram. These buds develop into a new organism which detaches them from the parent body at the time of maturation.
>Hydra is found in freshwater. It is small and has a tubular structure that is composed of tentacles. In hydra, budding involves a small bud which is developed from their parent hydra by the help of mitotic cell division.
>Small buds receive protein and nutrition from the parent hydra. They grow healthy and their growth starts by developing mouth and small tentacles. Finally, hydra separated from their parent body and became an independent organism.

Note:As budding is a type of asexual reproduction. So, a newly developed individual is a replica of their parents and they are genetically similar. Budding takes place in unicellular organisms as well as multicellular organisms. Both hydra and yeast can be reproduced by the help of budding.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




