
Briefly describe the stages in the clotting of blood.
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: A blood clot is a sticky gel-like component that is seen at the site of wounds. When the skin gets a cut, after some time the blood thickens and stops flowing. This is a result of a cascade of events caused by many proteins, enzymes, and a key vitamin.
Complete answer: Blood clotting is the process of converting liquid blood into a thick jelly-like substance. On being injured or getting cut over skin we see an immediate flow of blood from that site. If blood continuously flows in that way, we will eventually be deficient in the blood to survive. Thus, to stop excess blood flow various proteins and enzymes act to produce an effect to counteract the flow of blood. The platelets and proteins in plasma play a key role in inducing a cascade of events that will form a clot over the site of the cut.
Now let us understand the process of blood clotting with the help of a flow chart.
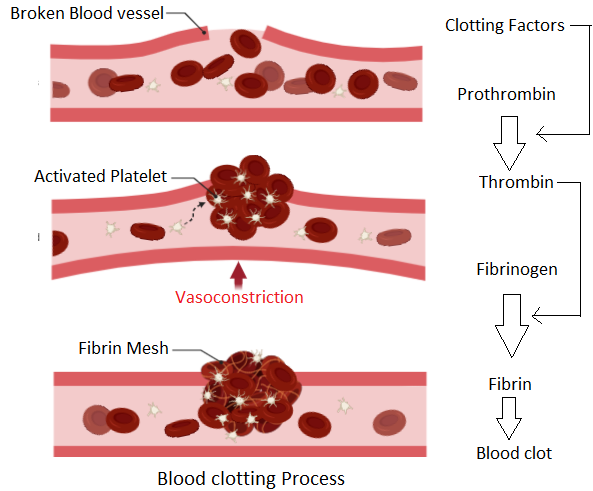
The process starts with a cut that damages the blood vessels. Platelets are a type of blood cell that produces prothrombin protein in the availability of vitamin K. The prothrombin then converts into its active form called thrombin by the activity of thrombokinase enzyme and calcium ions. After this, the thrombin acts to convert the non-functional or inactive form of fibrinogen protein into its active form called fibrin. Fibrin is an insoluble protein thus gives the blood a jelly-like appearance that does not flow easily. It forms a thread mesh-like structure over the site of blood vessel damage. So, this forms the clot.
Note: Blood clotting is an important phenomenon that takes place to prevent excess blood loss. Although the clots formed dissolves after some time when the damage heals. But sometimes the clots are formed inside the walls of blood vessels and do not dissolve. This causes blockage of the vessel and prevents normal blood flow.
Complete answer: Blood clotting is the process of converting liquid blood into a thick jelly-like substance. On being injured or getting cut over skin we see an immediate flow of blood from that site. If blood continuously flows in that way, we will eventually be deficient in the blood to survive. Thus, to stop excess blood flow various proteins and enzymes act to produce an effect to counteract the flow of blood. The platelets and proteins in plasma play a key role in inducing a cascade of events that will form a clot over the site of the cut.
Now let us understand the process of blood clotting with the help of a flow chart.

The process starts with a cut that damages the blood vessels. Platelets are a type of blood cell that produces prothrombin protein in the availability of vitamin K. The prothrombin then converts into its active form called thrombin by the activity of thrombokinase enzyme and calcium ions. After this, the thrombin acts to convert the non-functional or inactive form of fibrinogen protein into its active form called fibrin. Fibrin is an insoluble protein thus gives the blood a jelly-like appearance that does not flow easily. It forms a thread mesh-like structure over the site of blood vessel damage. So, this forms the clot.
Note: Blood clotting is an important phenomenon that takes place to prevent excess blood loss. Although the clots formed dissolves after some time when the damage heals. But sometimes the clots are formed inside the walls of blood vessels and do not dissolve. This causes blockage of the vessel and prevents normal blood flow.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




