
Bone-forming cells are known as
(a)Chondroclasts
(b)Osteoblasts
(c)Chondroblasts
(d)Osteoclasts
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The major cellular part of the bone is the bone-forming cells. They originate from the mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). MSC, along with adipocytes, and myocytes, among other types of cells, give rise to this cell. In the periosteum, the thin connective tissue layer on the outer surface of the bones, and in the endosteum, these cells are present in large numbers.
Complete answer:
The osteoblast is a large cell that is responsible for the bone synthesis and mineralization during bone formation and bone remodeling.
Osteoblasts are the cells that shape new bones. They also come from the bone marrow and are connected with structural cells. They've got just one nucleus. Osteoblasts act to develop bone in teams. They create fresh bone called "osteoid" made of bone collagen and other proteins. Then they control calcium and the deposition of minerals. On the surface of the new bone, they are located.
The cells become flat and look like pancakes when the team of osteoblasts has finished filling in a cavity. They line the bone's surface. Lining cells are often referred to as these old osteoblasts. The osteon is generally called a community of organized osteoblasts along with the bone formed by a unit of cells.
Osteoblasts that are buried in the matrix are referred to as osteocytes. The surface layer of osteoblasts during bone formation consists of cuboidal cells, called active osteoblasts. The surface osteoblasts are flattened when the bone-forming unit is not actively synthesizing bone, and are called inactive osteoblasts.
Additional Information: The chondroblast is a large multinucleated cell that is involved in calcified cartilage resorption.
The chondroblast is a cell that forms chondrocytes (called cartilage cells) derived from a mesenchymal stem cell.
The osteoclast is a large, multinucleated cell that is responsible for bone dissolution and absorption.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Osteoblasts’.
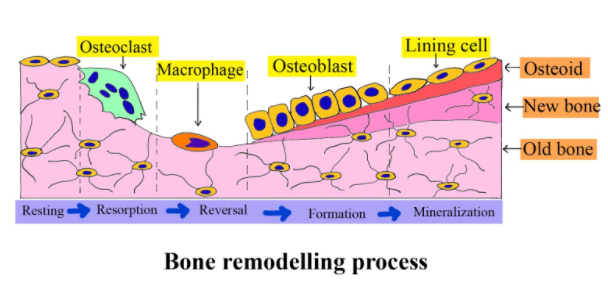
Note: Specialized, terminally differentiated mesenchymal stem cell products are osteoblasts. In much smaller amounts, they synthesize thick, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which make up the organic bone matrix.
Osteoblasts manufacture hydroxyapatite-the bone mineral that is deposited in a highly controlled way into the organic matrix that forms a solid and dense mineralized tissue-in structured groups of attached cells, the mineralized matrix. The principal support for the bodies of air-breathing vertebrates is the mineralized skeleton. This is an important store of minerals, both for acid-base balance and conservation of calcium or phosphate, for physiological homeostasis.
Complete answer:
The osteoblast is a large cell that is responsible for the bone synthesis and mineralization during bone formation and bone remodeling.
Osteoblasts are the cells that shape new bones. They also come from the bone marrow and are connected with structural cells. They've got just one nucleus. Osteoblasts act to develop bone in teams. They create fresh bone called "osteoid" made of bone collagen and other proteins. Then they control calcium and the deposition of minerals. On the surface of the new bone, they are located.
The cells become flat and look like pancakes when the team of osteoblasts has finished filling in a cavity. They line the bone's surface. Lining cells are often referred to as these old osteoblasts. The osteon is generally called a community of organized osteoblasts along with the bone formed by a unit of cells.
Osteoblasts that are buried in the matrix are referred to as osteocytes. The surface layer of osteoblasts during bone formation consists of cuboidal cells, called active osteoblasts. The surface osteoblasts are flattened when the bone-forming unit is not actively synthesizing bone, and are called inactive osteoblasts.
Additional Information: The chondroblast is a large multinucleated cell that is involved in calcified cartilage resorption.
The chondroblast is a cell that forms chondrocytes (called cartilage cells) derived from a mesenchymal stem cell.
The osteoclast is a large, multinucleated cell that is responsible for bone dissolution and absorption.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Osteoblasts’.

Note: Specialized, terminally differentiated mesenchymal stem cell products are osteoblasts. In much smaller amounts, they synthesize thick, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which make up the organic bone matrix.
Osteoblasts manufacture hydroxyapatite-the bone mineral that is deposited in a highly controlled way into the organic matrix that forms a solid and dense mineralized tissue-in structured groups of attached cells, the mineralized matrix. The principal support for the bodies of air-breathing vertebrates is the mineralized skeleton. This is an important store of minerals, both for acid-base balance and conservation of calcium or phosphate, for physiological homeostasis.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




