
Bonding in silicon is __________.
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: Silicon is commonly known as silicon dioxide or silica. Silica is present as the major constituent of earth’s crust. Pure forms of silicon exist as colourless solid, but impurity due to metal has some characteristic colour to the silicon.
Complete answer:
Silicon is known as covalent solid which is capable of forming a three-dimensional network. In the chemical structure of the silicon, each oxygen atom of silicon is bonded covalently with silicon atom. This fashion is repeated in three dimensions to create a huge network of silicon.
Silicon comes under the carbon family having atomic number $14$. Electronic configuration of silicon is written as $\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^2}$. From the electronic configuration of silicon, we can see that it contains $4$electron in its outermost shell. Hence, it requires four more electrons to complete its octet.
When silicon combines with an oxygen atom despite forming a double bond as formed between $\left( {C = O} \right)$, Silicon forms a single bond with the oxygen atom. The main reason behind formation of this single bond is that the size of $3p$ orbital is quite large with respect to the size of $2p$ orbital of the oxygen atom. This size difference between the orbital of silicon and oxygen restricts the effective overlapping between the atoms. Therefore, to satisfy the valency of silicon it combines with oxygen atom with a single bond.
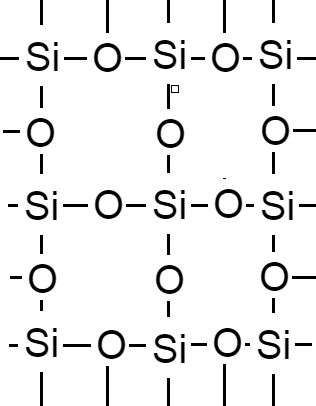
Hence, in a network one silicon atom forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms.
Therefore, we can say that bonding in silicon is covalent bonding.
Note:
Due to formation of this huge network silicon is non-reactive in nature. Silica exists in different crystallographic forms such as quartz, cristobalite and tridymite. All of these forms of silica are interconvertible with each other and show different structures.
Complete answer:
Silicon is known as covalent solid which is capable of forming a three-dimensional network. In the chemical structure of the silicon, each oxygen atom of silicon is bonded covalently with silicon atom. This fashion is repeated in three dimensions to create a huge network of silicon.
Silicon comes under the carbon family having atomic number $14$. Electronic configuration of silicon is written as $\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^2}$. From the electronic configuration of silicon, we can see that it contains $4$electron in its outermost shell. Hence, it requires four more electrons to complete its octet.
When silicon combines with an oxygen atom despite forming a double bond as formed between $\left( {C = O} \right)$, Silicon forms a single bond with the oxygen atom. The main reason behind formation of this single bond is that the size of $3p$ orbital is quite large with respect to the size of $2p$ orbital of the oxygen atom. This size difference between the orbital of silicon and oxygen restricts the effective overlapping between the atoms. Therefore, to satisfy the valency of silicon it combines with oxygen atom with a single bond.
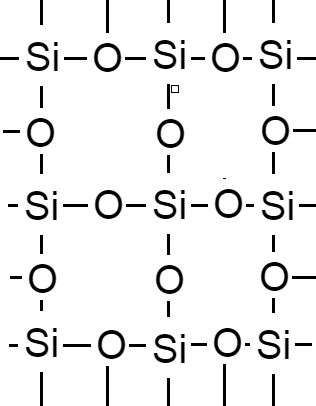
Hence, in a network one silicon atom forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms.
Therefore, we can say that bonding in silicon is covalent bonding.
Note:
Due to formation of this huge network silicon is non-reactive in nature. Silica exists in different crystallographic forms such as quartz, cristobalite and tridymite. All of these forms of silica are interconvertible with each other and show different structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




