
Bond order of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 0
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: According to the molecular orbital theory, the bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds in a molecule. Bond order is equal to half of the difference between the number of electrons in bonding (\[{{N}_{b}}\]) and antibonding molecular orbitals (\[{{N}_{a}}\]).
Complete Solution :
\[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule will be formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals of two beryllium atoms.
A Be atom has four electrons. It has two valence electrons and its electronic configuration is \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}\]. Therefore, \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has eight electrons which are to be filled in four molecular orbitals.
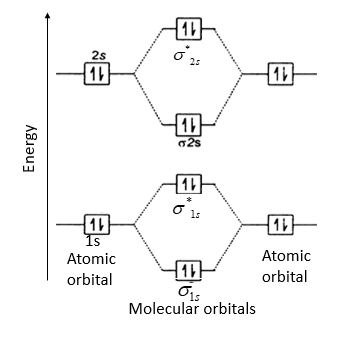
Thus, electronic configuration of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is \[{{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}\]
Here, bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{b}}\] = 4 and anti-bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{a}}\]= 4
Therefore, bond order (B.O.) of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\frac{1}{2}({{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}) \\
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\frac{1}{2}(4-4)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
- Zero value of bond order corresponds to non-existence of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The bond order of a molecule conveys the following information:
1. The stability of a molecule can also be expressed in terms of bond order. Higher the bond order, more stable is the molecule.
2. Bond length: Bond order and bond length are inversely related. Thus, higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length and vice-versa.
3. Bond dissociation energy: Bond order in a molecule is directly proportional to its bond dissociation energy. Greater the bond order, more will be the value of bond dissociation energy.
Complete Solution :
\[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule will be formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals of two beryllium atoms.
A Be atom has four electrons. It has two valence electrons and its electronic configuration is \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}\]. Therefore, \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has eight electrons which are to be filled in four molecular orbitals.

Thus, electronic configuration of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] is \[{{\left( \sigma 1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}1s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( \sigma 2s \right)}^{2}}{{\left( {{\sigma }^{*}}2s \right)}^{2}}\]
Here, bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{b}}\] = 4 and anti-bonding electrons, \[{{N}_{a}}\]= 4
Therefore, bond order (B.O.) of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\frac{1}{2}({{N}_{b}}-{{N}_{a}}) \\
& \text{B}\text{.O}\text{.}=\frac{1}{2}(4-4)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
- Zero value of bond order corresponds to non-existence of \[\text{B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The bond order of a molecule conveys the following information:
1. The stability of a molecule can also be expressed in terms of bond order. Higher the bond order, more stable is the molecule.
2. Bond length: Bond order and bond length are inversely related. Thus, higher the bond order, shorter is the bond length and vice-versa.
3. Bond dissociation energy: Bond order in a molecule is directly proportional to its bond dissociation energy. Greater the bond order, more will be the value of bond dissociation energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




