
Why is the boiling point of alcohol greater than that of ketones and aldehydes?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: The bond which is formed in a molecule between hydrogen atom and electronegative atom is considered as hydrogen bonding which is of two types: intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete answer:
Alcohol is a hydroxyl group containing compounds which shows various similarities as well as differences with carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones.
As we know aldehyde and ketones are polar compounds and they have sufficient intermolecular dipole-dipole interaction. This interaction is formed between the carbonyl groups $ \left( {C = O} \right) $ of two molecules of aldehyde and ketones.
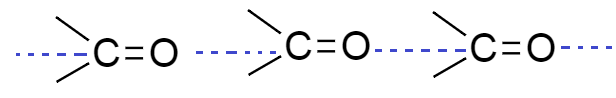
From the above diagram we see that dipole interaction is formed between two different molecules of aldehyde and ketone; they form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Alcohols are polar compounds due to the presence of hydroxyl groups and they have sufficient intermolecular interaction. The strength of dipole-dipole interaction is higher in the case of alcohol due to the large difference between electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen atoms $ \left( {O - H} \right) $ .

Due to high dipole-dipole interaction, molecules of alcohol are capable of intermolecular hydrogen bonding and exist as associated molecules.
This associated molecule requires a large amount of energy to break the hydrogen bond which is formed in the molecule network therefore, the melting point of the alcohol molecule is high.
$ \Rightarrow $ The boiling point of alcohol is greater than that of ketones and aldehydes due to stronger hydrogen bonding.
Note:
Alkanals synonym is used for aldehyde while alkenones is used for ketones. Boiling point of alcohol is higher than ether molecules with the same molecular masses. Boiling point of aldehyde and ketone is also less than carboxylic acid.
Complete answer:
Alcohol is a hydroxyl group containing compounds which shows various similarities as well as differences with carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones.
As we know aldehyde and ketones are polar compounds and they have sufficient intermolecular dipole-dipole interaction. This interaction is formed between the carbonyl groups $ \left( {C = O} \right) $ of two molecules of aldehyde and ketones.

From the above diagram we see that dipole interaction is formed between two different molecules of aldehyde and ketone; they form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Alcohols are polar compounds due to the presence of hydroxyl groups and they have sufficient intermolecular interaction. The strength of dipole-dipole interaction is higher in the case of alcohol due to the large difference between electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen atoms $ \left( {O - H} \right) $ .

Due to high dipole-dipole interaction, molecules of alcohol are capable of intermolecular hydrogen bonding and exist as associated molecules.
This associated molecule requires a large amount of energy to break the hydrogen bond which is formed in the molecule network therefore, the melting point of the alcohol molecule is high.
$ \Rightarrow $ The boiling point of alcohol is greater than that of ketones and aldehydes due to stronger hydrogen bonding.
Note:
Alkanals synonym is used for aldehyde while alkenones is used for ketones. Boiling point of alcohol is higher than ether molecules with the same molecular masses. Boiling point of aldehyde and ketone is also less than carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




