
Blood cell without nucleus are
(a)Red blood corpuscles
(b)White blood corpuscles
(c)Blood platelets
(d)None of these
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: These cells carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues in human beings. They also bring carbon dioxide back to the lungs to finally be removed from the body. The average lifespan of these cells is around 120 days.
Complete answer:
Mature red blood corpuscles (RBCs) are the blood cells without a nucleus, found within all mammals including human beings. The red blood cells are also called erythrocytes.
Additional Information:
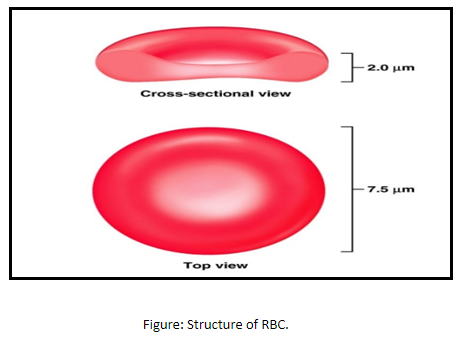
-A mature human red blood cell is small, round, and biconcave and appears dumbbell-shaped.
-The biconcave shape of the cell allows oxygen exchange at a constant rate and over the largest possible area.
-RBCs are flexible and assume a bell shape as it passes through extremely small blood vessels.
-The large flexibility of the RBCs is primarily due to the cell membrane, as there are no organelles and filaments inside the cell.
-The red cell develops in the bone marrow in several stages from a cell called hemocytoblast.
-There are some 5.2 million red blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood in the adult human.
-Spleen is known as the graveyard of the RBCs. The old red blood cells are recycled in the spleen, and platelets and white blood cells are stored there.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Red blood corpuscles.’
Note: It is covered with a membrane composed of lipids and proteins, lacks a nucleus, and contains hemoglobin—a red iron-rich protein that binds oxygen. The mammalian red blood cell is further adapted by lacking a nucleus—the amount of oxygen required by the cell for its metabolism is thus very low, and most oxygen carried can be freed into the tissues.
Complete answer:
Mature red blood corpuscles (RBCs) are the blood cells without a nucleus, found within all mammals including human beings. The red blood cells are also called erythrocytes.

Additional Information:
-A mature human red blood cell is small, round, and biconcave and appears dumbbell-shaped.
-The biconcave shape of the cell allows oxygen exchange at a constant rate and over the largest possible area.
-RBCs are flexible and assume a bell shape as it passes through extremely small blood vessels.
-The large flexibility of the RBCs is primarily due to the cell membrane, as there are no organelles and filaments inside the cell.
-The red cell develops in the bone marrow in several stages from a cell called hemocytoblast.
-There are some 5.2 million red blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood in the adult human.
-Spleen is known as the graveyard of the RBCs. The old red blood cells are recycled in the spleen, and platelets and white blood cells are stored there.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Red blood corpuscles.’
Note: It is covered with a membrane composed of lipids and proteins, lacks a nucleus, and contains hemoglobin—a red iron-rich protein that binds oxygen. The mammalian red blood cell is further adapted by lacking a nucleus—the amount of oxygen required by the cell for its metabolism is thus very low, and most oxygen carried can be freed into the tissues.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




