
Block diagram of a receiver is shown in the figure:
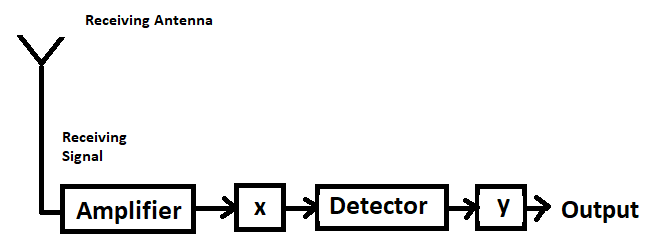
(A) Identify 'X' and 'Y'
(B) Write their functions.

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Carrier modulation allows the transmission of modulating frequencies without the use of transmission wire as a medium. However, in order to make the communication process complete or to be useful, the intelligence must be recovered in its original form at the receiving end. Demodulation or detection is the process of recreating the original modulating frequency from the RF carriers. The figure given in the above question represents the process of demodulation of a typical receiver.
Complete step by step answer:
By studying the block diagram for the process of demodulation of a receiver we can easily conclude that the unknown block X represents the intermediate frequency (IF) stage. The unknown block Y on the other hand represents an amplifier.
Thus the correct answer to question (A) is that X is the Intermediate Frequency (IF) and Y is an amplifier.
We know that in the Intermediate frequency stage or the IF stage, the frequency of the carrier or the carrier frequency is converted or transformed from a higher frequency to a lower frequency. After, the carrier frequency is converted to a lower frequency only then can the detector detect the modulated signal. The function of the amplifier is to increase the frequency of the modulated carrier wave which was decreased by the IF in the Intermediate frequency stage and supply it to the output.
Thus, these are the functions of the Intermediate frequency or IF (X) and the amplifier (Y).
Note: The output of an ideal detector must be an exact reproduction of the modulation or intelligence existing on the RF wave. Failure to accurately recover this intelligence will result in distortion and degradation of the demodulated signal and intelligence will be lost. The distortion may be in amplitude, frequency, or phase, depending on the nature of the demodulator.
Complete step by step answer:
By studying the block diagram for the process of demodulation of a receiver we can easily conclude that the unknown block X represents the intermediate frequency (IF) stage. The unknown block Y on the other hand represents an amplifier.
Thus the correct answer to question (A) is that X is the Intermediate Frequency (IF) and Y is an amplifier.
We know that in the Intermediate frequency stage or the IF stage, the frequency of the carrier or the carrier frequency is converted or transformed from a higher frequency to a lower frequency. After, the carrier frequency is converted to a lower frequency only then can the detector detect the modulated signal. The function of the amplifier is to increase the frequency of the modulated carrier wave which was decreased by the IF in the Intermediate frequency stage and supply it to the output.
Thus, these are the functions of the Intermediate frequency or IF (X) and the amplifier (Y).
Note: The output of an ideal detector must be an exact reproduction of the modulation or intelligence existing on the RF wave. Failure to accurately recover this intelligence will result in distortion and degradation of the demodulated signal and intelligence will be lost. The distortion may be in amplitude, frequency, or phase, depending on the nature of the demodulator.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




