
Benzonitrile on reaction with ${C_2}{H_5}MgBr$, followed by hydrolysis, gives:
A.
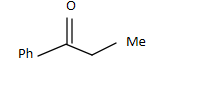
B.
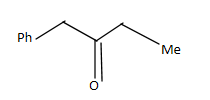
C.
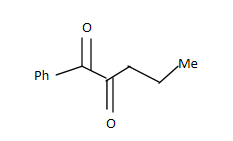
D.
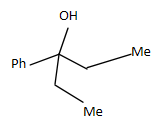




Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint:${C_2}{H_5}MgBr$ is known as Grignard reagent , so think about the reactions between Grignard reagent and aliphatic or aromatic nitriles. Addition of Grignard reagent to nitriles gives ketones after hydrolysis.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of Grignard reagents with nitriles is,
$R - C \equiv N\xrightarrow[{{H_3}{O^ + }}]{{R' - MgX}}R - CO - R'$
So the reaction between benzonitrile and ${C_2}{H_5}MgBr$ gives,
$Ph - C \equiv N + {C_2}{H_5}MgBr\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}Ph - CO - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$
So the answer is A.
Additional Information:- The Grignard reaction is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl or aryl–magnesium halides add to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran, which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. Grignard reagents are prepared by treating an organic halide with magnesium metal. Cyclic or acyclic ethers are required to stabilize the organomagnesium compound. The reaction to form Grignard reagents involves the use of magnesium ribbon. All magnesium is coated with a passivating layer of magnesium oxide, which inhibits reactions with the organic halide. Grignard reagents are more sensitive to moisture and oxygen. Grignard reagents are nucleophiles in nucleophilic aliphatic substitutions. Grignard reagents serve as a base for protic substances.
Note:
Grignard reagents are basic and react with alcohols, phenols to give alkoxides. In the reaction between aromatic nitriles and Grignard reagent at first the imine salt is formed and then the produced imine salt reacts with water to give ketone.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of Grignard reagents with nitriles is,
$R - C \equiv N\xrightarrow[{{H_3}{O^ + }}]{{R' - MgX}}R - CO - R'$
So the reaction between benzonitrile and ${C_2}{H_5}MgBr$ gives,
$Ph - C \equiv N + {C_2}{H_5}MgBr\xrightarrow{{{H_3}{O^ + }}}Ph - CO - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$
So the answer is A.
Additional Information:- The Grignard reaction is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl or aryl–magnesium halides add to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran, which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. Grignard reagents are prepared by treating an organic halide with magnesium metal. Cyclic or acyclic ethers are required to stabilize the organomagnesium compound. The reaction to form Grignard reagents involves the use of magnesium ribbon. All magnesium is coated with a passivating layer of magnesium oxide, which inhibits reactions with the organic halide. Grignard reagents are more sensitive to moisture and oxygen. Grignard reagents are nucleophiles in nucleophilic aliphatic substitutions. Grignard reagents serve as a base for protic substances.
Note:
Grignard reagents are basic and react with alcohols, phenols to give alkoxides. In the reaction between aromatic nitriles and Grignard reagent at first the imine salt is formed and then the produced imine salt reacts with water to give ketone.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




