
Based on the group valency of elements state the formula for the following giving justification for each: -
(a)- Oxides of 1st group elements.
(b)- Halides of the elements of group 13
(c)- Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of group 16
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The formula can be formulated by the crisscross method of the valency of the elements. The valency of group 1 is +1. The valency of group 13 is +3. The valency of group 2 is +2. The valency of group 16 is -2.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical properties and the physical properties of a group are similar. They have common outer electronic configuration due to which they have common valence or oxidation state.
So, with the valency of the compounds, we can formulate the formula of elements of a group with the element of other groups. This can be done by crisscross.
(i)- Oxides of 1st group elements.
The outer electronic configuration of 1st group elements is $n{{s}^{1}}$. So, their valency is 1. The oxygen has a valency of -2. So it can be crisscrossed.
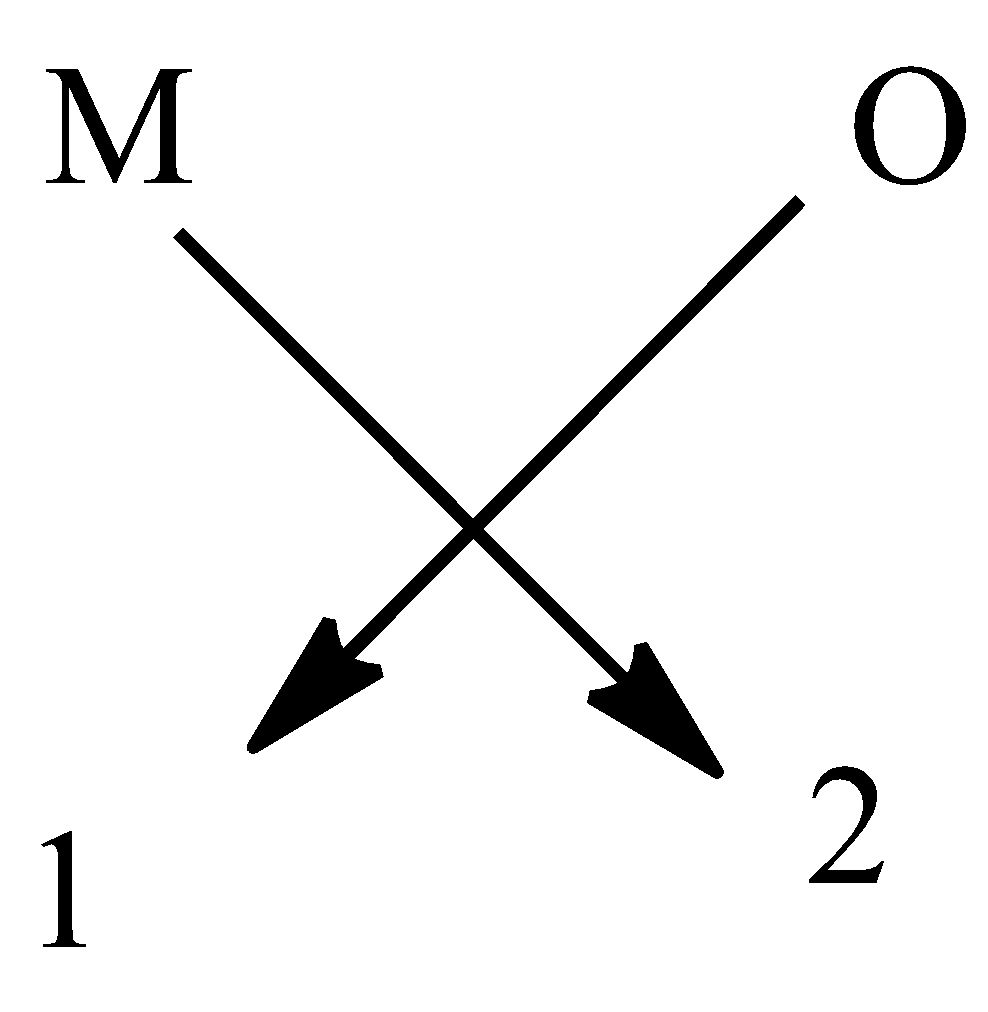
So, it has a formula${{M}_{2}}O$. It is done to complete the octet of the elements.
An example $L{{i}_{2}}O$ is a compound of the oxide of group 1.
(ii)- Halides of the elements of group 13
The outer electronic configuration of group 13 is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{1}}$ hence, their valency is +3. The halogens have a valency of -1. So, it can be crisscrossed.
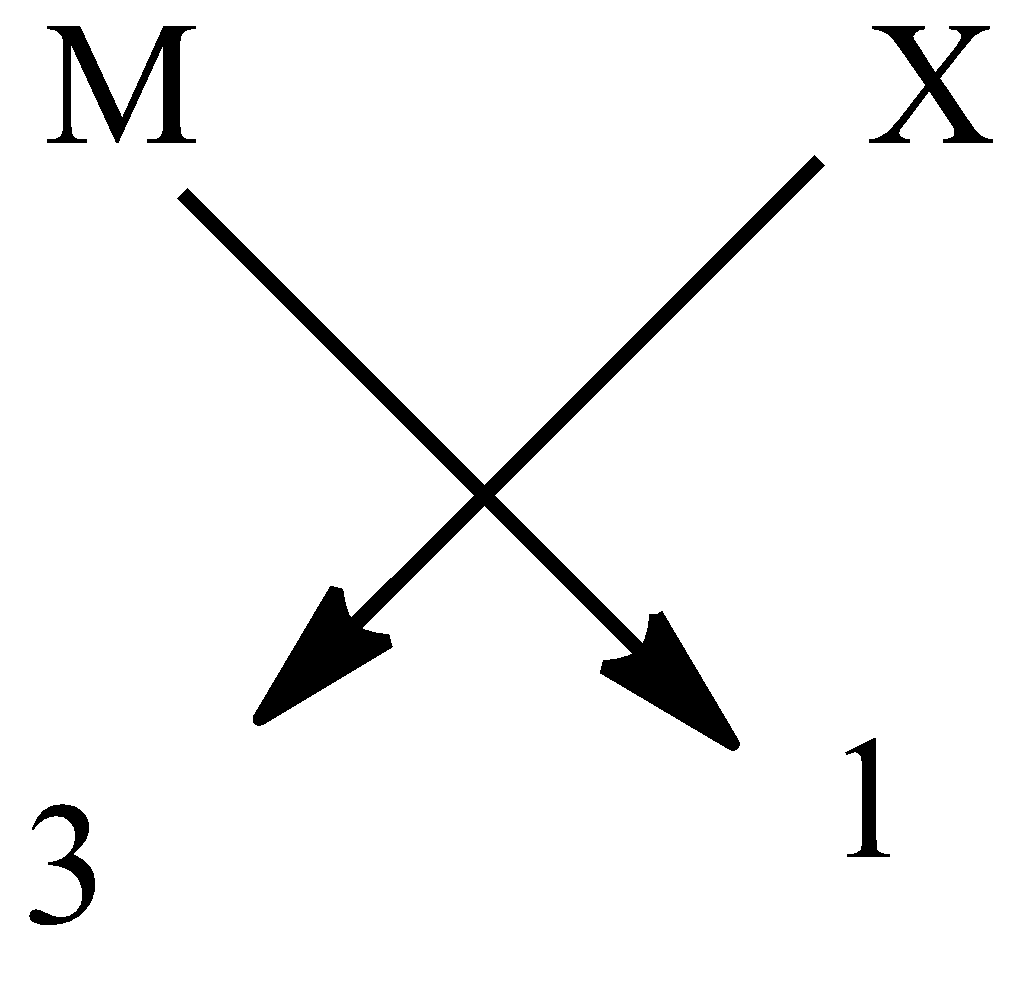
Hence, the formula is $M{{X}_{3}}$. It is done to complete the octet of the elements.
An example $B{{F}_{3}}$ is a halide of group 13.
(iii)- Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of group 16
The outer electronic configuration of group 2 is $n{{s}^{2}}$ so it has a valency +2 and the outer electronic configuration of group 16 is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$ so it has valency -2.
Hence the electrons donated by group 2 will be accepted by group 16, therefore, the formula will be $MO$.
$CaO$ is an example of group 2 with group 16.
Note: The sodium of group forms peroxide with oxygen ($N{{a}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ ) and the other metal like potassium, rubidium, and francium forms peroxide with oxygen ($M{{O}_{2}}$ ) because the reactivity of oxygen increases down the group.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical properties and the physical properties of a group are similar. They have common outer electronic configuration due to which they have common valence or oxidation state.
So, with the valency of the compounds, we can formulate the formula of elements of a group with the element of other groups. This can be done by crisscross.
(i)- Oxides of 1st group elements.
The outer electronic configuration of 1st group elements is $n{{s}^{1}}$. So, their valency is 1. The oxygen has a valency of -2. So it can be crisscrossed.

So, it has a formula${{M}_{2}}O$. It is done to complete the octet of the elements.
An example $L{{i}_{2}}O$ is a compound of the oxide of group 1.
(ii)- Halides of the elements of group 13
The outer electronic configuration of group 13 is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{1}}$ hence, their valency is +3. The halogens have a valency of -1. So, it can be crisscrossed.

Hence, the formula is $M{{X}_{3}}$. It is done to complete the octet of the elements.
An example $B{{F}_{3}}$ is a halide of group 13.
(iii)- Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of group 16
The outer electronic configuration of group 2 is $n{{s}^{2}}$ so it has a valency +2 and the outer electronic configuration of group 16 is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$ so it has valency -2.
Hence the electrons donated by group 2 will be accepted by group 16, therefore, the formula will be $MO$.
$CaO$ is an example of group 2 with group 16.
Note: The sodium of group forms peroxide with oxygen ($N{{a}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ ) and the other metal like potassium, rubidium, and francium forms peroxide with oxygen ($M{{O}_{2}}$ ) because the reactivity of oxygen increases down the group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




