
What is bacteriophage? Explain lytic cycle of bacteriophage with a suitable diagram.
Answer
467.1k+ views
Hint: A virus is an infectious agent. The agents are viable only within the host organism. Viruses cause a wide variety of infections in almost all higher organisms as well as bacteria.
Complete answer:
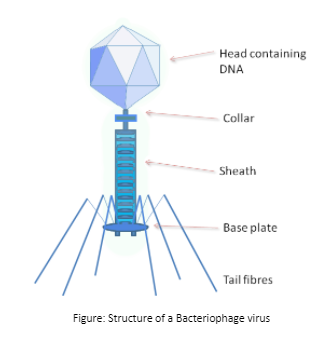
Viruses which infect bacterial cells are known as Bacteriophage viruses. The term bacteriophage means “bacteria eater”. These viruses infect the bacterial cells and eventually destroy them. The genetic material present in these viruses can be either DNA or RNA. The genetic material is covered by a protein capsule.
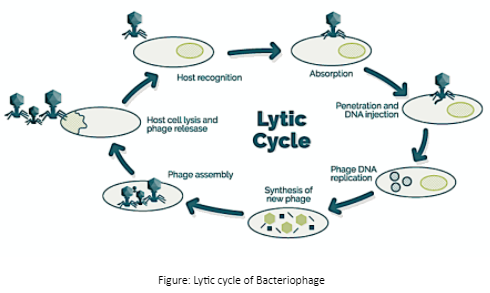
Lytic cycle of Bacteriophage: The reproductive cycle of Bacteriophage viruses are known as Lytic cycle. The cycle consists of six stages.
Stage 1 Attachment: In the first stage the virus attaches itself to the surface of the host bacterial cell and prepares to inject its DNA into the host cell.
Stage 2 Penetration: The virus injects its genetic material (either DNA or RNA) into the host cell by penetrating the host cell membrane.
Stage 3 Transcription: The virus degrades the host’s DNA and alters the host cell’s biosynthesis to initiate the viral biosynthesis.
Stage 4 Biosynthesis: Replication of the viral genome takes place.
Stage 5 Maturation: Assembling of the replicated material to fully developed viral phages.
Stage 6 Lysis: The infected host cell bursts releasing the newly formed viral cells.
Note: Another life cycle exhibited by bacteriophage viruses is known as lysogenic cycle. Unlike lytic cycle lysogenic cycle do not result in the immediate lysis and destruction of the host cells. The viral genome integrates with the host genome and starts replicating. The virus gets active once the nutrients in host cell depletes and eventually the reproductive cycle of the virus is initiated.
Complete answer:
Viruses which infect bacterial cells are known as Bacteriophage viruses. The term bacteriophage means “bacteria eater”. These viruses infect the bacterial cells and eventually destroy them. The genetic material present in these viruses can be either DNA or RNA. The genetic material is covered by a protein capsule.

Lytic cycle of Bacteriophage: The reproductive cycle of Bacteriophage viruses are known as Lytic cycle. The cycle consists of six stages.
Stage 1 Attachment: In the first stage the virus attaches itself to the surface of the host bacterial cell and prepares to inject its DNA into the host cell.
Stage 2 Penetration: The virus injects its genetic material (either DNA or RNA) into the host cell by penetrating the host cell membrane.
Stage 3 Transcription: The virus degrades the host’s DNA and alters the host cell’s biosynthesis to initiate the viral biosynthesis.
Stage 4 Biosynthesis: Replication of the viral genome takes place.
Stage 5 Maturation: Assembling of the replicated material to fully developed viral phages.
Stage 6 Lysis: The infected host cell bursts releasing the newly formed viral cells.

Note: Another life cycle exhibited by bacteriophage viruses is known as lysogenic cycle. Unlike lytic cycle lysogenic cycle do not result in the immediate lysis and destruction of the host cells. The viral genome integrates with the host genome and starts replicating. The virus gets active once the nutrients in host cell depletes and eventually the reproductive cycle of the virus is initiated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




