
Bacteria differs from eukaryotes in the absence of
(A)DNA
(B)Basic proteins
(C)Histones
(D)Both B and C
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: In bacteria, the DNA is mostly a single circular molecule. As DNA is very long, it needs to be compressed to get stored properly. Bacteria compress their DNA into smaller spaces through supercoiling with help of some basic proteins.
Complete answer:
In eukaryotes, the protein that binds DNA is is known as histone but in Bacteria i.e prokaryotes, proteins which bind DNA is not histone but it is a histone-like protein as it’s most of the biochemical property resembles that of the eukaryotic histone protein.
Additional Information: Bacteria i.e prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes not only in absence of histone protein but also in many other criteria. For example, bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles like Mitochondria, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and even the true nucleus is also absent in bacteria. Instead of a true nucleus, bacteria have a nucleoid that is irregular in shape and contains most of the genetic information. Like the nucleus, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Sexual reproduction is absent in bacteria. They replicate by binary fission i.e asexually. Many bacteria also contain the capsule made up of carbohydrates which help them to increase disease-causing ability as they can easily escape from macrophages i.e engulfing cells because the capsule is present.
So, the correct answer is 'Histones’.
Note: Other than bacterial DNA, bacteria also contain some small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule which is known as a Plasmid. Plasmids are not necessary for living but give a genetic advantage to bacteria. For example, it provides antibiotic resistance to bacteria.
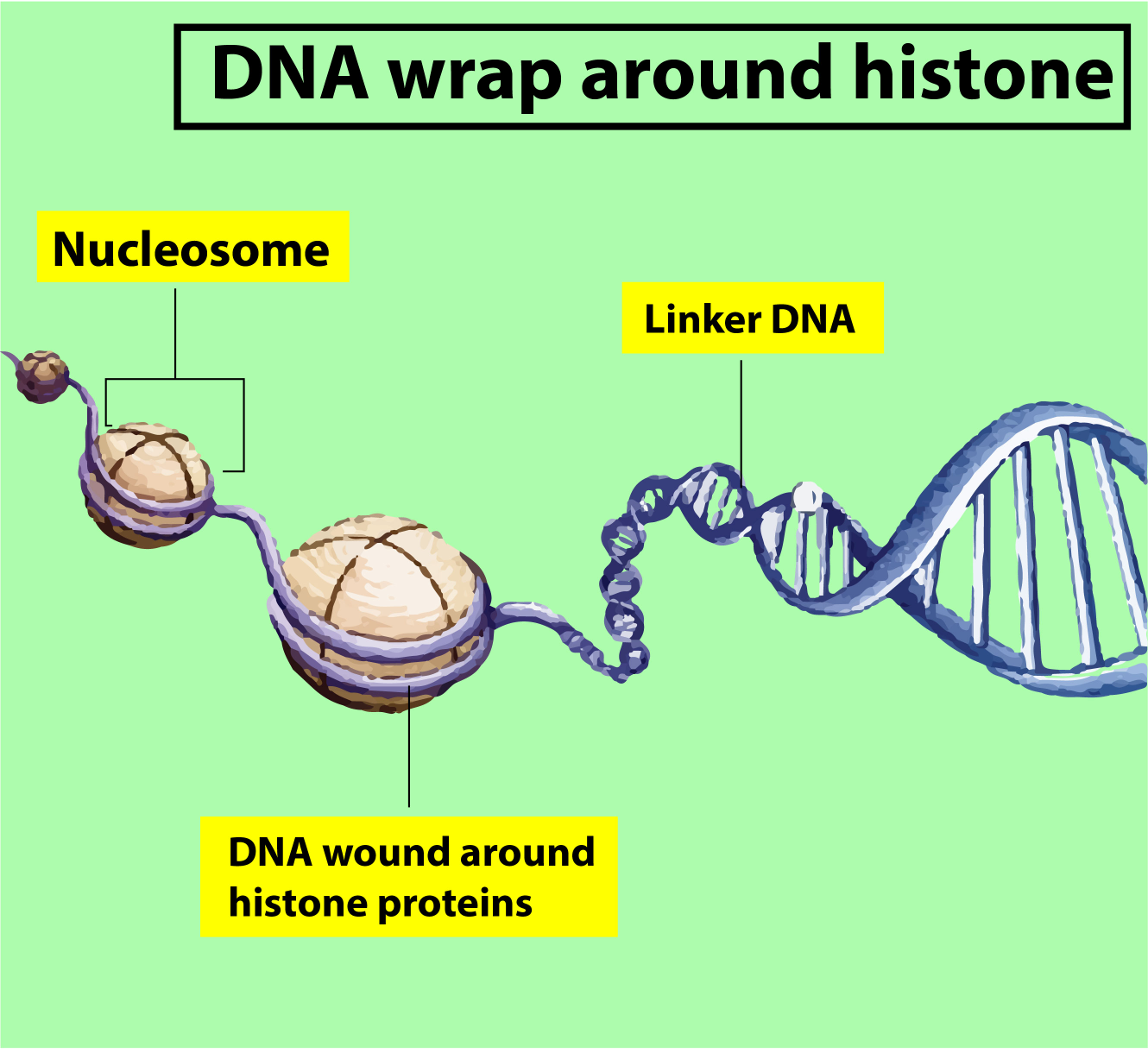
Complete answer:
In eukaryotes, the protein that binds DNA is is known as histone but in Bacteria i.e prokaryotes, proteins which bind DNA is not histone but it is a histone-like protein as it’s most of the biochemical property resembles that of the eukaryotic histone protein.
Additional Information: Bacteria i.e prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes not only in absence of histone protein but also in many other criteria. For example, bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles like Mitochondria, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and even the true nucleus is also absent in bacteria. Instead of a true nucleus, bacteria have a nucleoid that is irregular in shape and contains most of the genetic information. Like the nucleus, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Sexual reproduction is absent in bacteria. They replicate by binary fission i.e asexually. Many bacteria also contain the capsule made up of carbohydrates which help them to increase disease-causing ability as they can easily escape from macrophages i.e engulfing cells because the capsule is present.
So, the correct answer is 'Histones’.
Note: Other than bacterial DNA, bacteria also contain some small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule which is known as a Plasmid. Plasmids are not necessary for living but give a genetic advantage to bacteria. For example, it provides antibiotic resistance to bacteria.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




