
Where can Axile Placentation be seen?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint:Placentation is defined as the arrangement of ovules inside the ovary. In the flowering plants, there are numerous types of placentation. Free central (septa is absent), parietal (ovules at inner wall or periphery), marginal (ovules at ridge through the ventral suture of ovary), axile (around the ovary’s centre) and basal (in base of ovary) are the different types of placentation.
Complete answer:
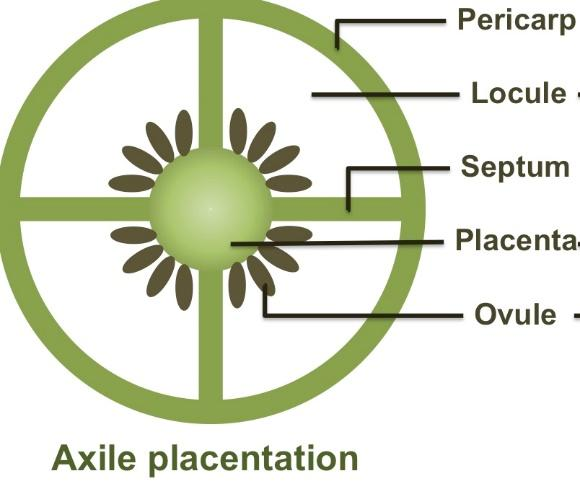
The ovules are axial in the axial placentation. China rose, tomato, cotton and lemon are the examples of the plants exhibiting axial placentation. It is usually seen in multilocular ovaries, where the placentation is present along the axis of the fusion of ovaries. The arrangement is common in liliaceae, rutaceae and solanaceae families. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis exhibits axial placentation. The ovules are arranged along the placenta's central axis. Radial spokes section the ovary with placentae in distinct locules. The number of chambers present is equivalent to the number of carpels. The placentation can be seen in bicarpellary, multicarpellary and multilocular ovaries. It occurs in syncarpous pistils. Ovaries are divided into two or more chambers. Placenta occurs in the centre, where the septae get together, forming axile columns with the formation of ovules. In shoe flowers (pentalocular), it can be seen. In lemon, around the compound ovary, ovules are seen on an axis, which are formed from a jointed septae.
Note:
Ovules are attached inside the flower’s ovary via funiculi. Funiculi is the counterpart of umbilical cord. The funiculi attach to the part of the ovary, which is called the placenta. Placentation’s main function is to connect walls of the ovary with the flower. Placenta helps in providing nutrients to the developing embryo. It serves as a cushion-like structure for connection.
Complete answer:
The ovules are axial in the axial placentation. China rose, tomato, cotton and lemon are the examples of the plants exhibiting axial placentation. It is usually seen in multilocular ovaries, where the placentation is present along the axis of the fusion of ovaries. The arrangement is common in liliaceae, rutaceae and solanaceae families. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis exhibits axial placentation. The ovules are arranged along the placenta's central axis. Radial spokes section the ovary with placentae in distinct locules. The number of chambers present is equivalent to the number of carpels. The placentation can be seen in bicarpellary, multicarpellary and multilocular ovaries. It occurs in syncarpous pistils. Ovaries are divided into two or more chambers. Placenta occurs in the centre, where the septae get together, forming axile columns with the formation of ovules. In shoe flowers (pentalocular), it can be seen. In lemon, around the compound ovary, ovules are seen on an axis, which are formed from a jointed septae.

Note:
Ovules are attached inside the flower’s ovary via funiculi. Funiculi is the counterpart of umbilical cord. The funiculi attach to the part of the ovary, which is called the placenta. Placentation’s main function is to connect walls of the ovary with the flower. Placenta helps in providing nutrients to the developing embryo. It serves as a cushion-like structure for connection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




