
What is the average bond order in the sulphate ion?
Answer
532.5k+ views
Hint: Formula of sulphate ion is \[S{{O}_{4}}^{2-}\]. Bond order is the number of covalent bonds shared between two atoms. Resonance is possible in sulphate ions, so be careful while calculating the bond order.
Structure of sulphate ion:
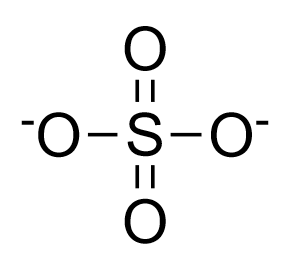
Complete answer:
-Bond order can be integer as well as fraction. For example, In case of Nitrogen \[\left( N\equiv N \right)\], the bond order is , as there are \[3\] bonds between the two nitrogen atoms. But it can be fractional also where resonance is taking place. There are various methods to calculate bond order like molecular orbital theory, but for this question we’ll stick to one formula which is
-Bond order \[=\] Number of resonating bonds/Number of resonating structures
Where, the number of resonating bonds are those bonds which are involved in resonance.
-So, in this question, when you will draw all the resonating structures of sulphate ion(You just have to keep moving the negative charge on oxygen and form the subsequent resonating structures). You will notice all the bonds were involved in resonance, which means, number of resonating bonds are \[6\] in number and there are a total of \[4\]resonating structures(including the original structure)
Therefore, the bond order \[=\frac{6}{4}=1.5\]
Note:
Bond order is used as an indicator of stability of a chemical bond between two atoms. Higher the bond order, higher is the stability of that molecule and bond order is often used to compare the stability of molecules. Bond order can be zero also, for example in \[H{{e}_{2}},B{{e}_{2}}\] bond order is zero which can be explained by molecular orbital theory.
Structure of sulphate ion:

Complete answer:
-Bond order can be integer as well as fraction. For example, In case of Nitrogen \[\left( N\equiv N \right)\], the bond order is , as there are \[3\] bonds between the two nitrogen atoms. But it can be fractional also where resonance is taking place. There are various methods to calculate bond order like molecular orbital theory, but for this question we’ll stick to one formula which is
-Bond order \[=\] Number of resonating bonds/Number of resonating structures
Where, the number of resonating bonds are those bonds which are involved in resonance.
-So, in this question, when you will draw all the resonating structures of sulphate ion(You just have to keep moving the negative charge on oxygen and form the subsequent resonating structures). You will notice all the bonds were involved in resonance, which means, number of resonating bonds are \[6\] in number and there are a total of \[4\]resonating structures(including the original structure)
Therefore, the bond order \[=\frac{6}{4}=1.5\]
Note:
Bond order is used as an indicator of stability of a chemical bond between two atoms. Higher the bond order, higher is the stability of that molecule and bond order is often used to compare the stability of molecules. Bond order can be zero also, for example in \[H{{e}_{2}},B{{e}_{2}}\] bond order is zero which can be explained by molecular orbital theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




