
At which of the following stages of cell division, the separation of chromatids and their movement to opposite poles occur?
A. Prophase
B. Anaphase
C. Metaphase
D. Telophase
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: It is the third stage of the cell division in which the bridge is formed to separate the chromatids. It is the characteristic stage that occurs before the telophase stage in the cell cycle and also moves the chromatids apart.
Complete answer:
The stage of cell division when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are pulled to the opposite poles by the spindle fibers of the cell is called the Anaphase stage. It is a stage of mitosis or meiosis after the process of metaphase.
Additional Information: -Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
-There are two distinct types of cell division:
(a)A vegetative division, where each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis)
(b)A reproductive division, where the number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the daughter cells to produce haploid gametes (meiosis).
-Anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the chromosomes are segregated to opposite poles of the cell.
-Anaphase starts after the cell passes the spindle formation checkpoint, which allows chromosomes or chromatids to separate.
-In meiosis the Anaphase is divided into two stages: Anaphase I and Anaphase II.
So, the correct answer is ‘Anaphase’.
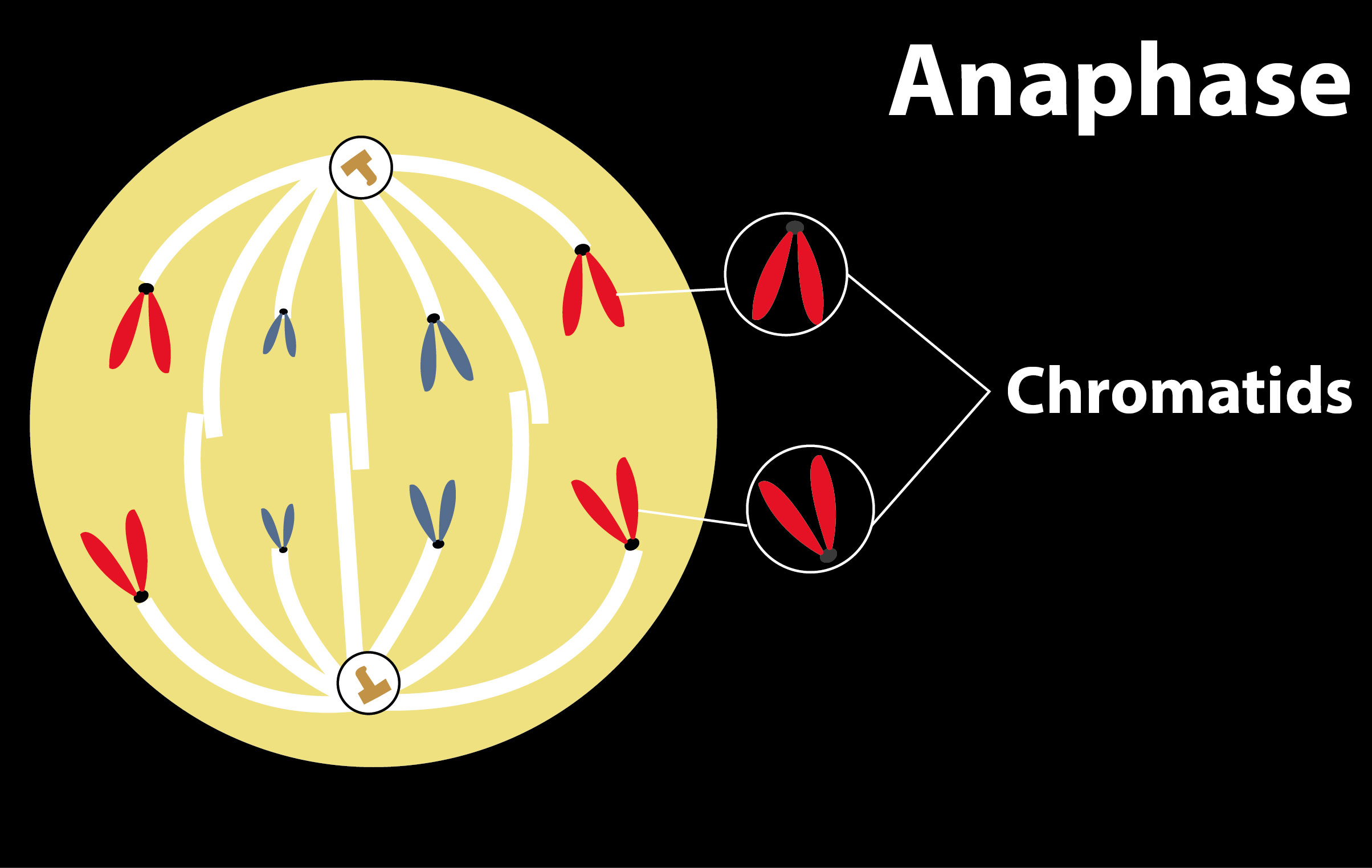
Note: Cell division consists of various stages: Prophase – first stage of division. Chromatin threads condense to form shorter more visible strands called chromosomes. Metaphase – chromosomes arrange themselves on the metaphase plate in the middle of the cell. Anaphase – very short stage of the cell, the chromosomes split and the sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell. Telophase – last stage of the cell cycle, separation of daughter cells by formation of the cell plate.
Complete answer:
The stage of cell division when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are pulled to the opposite poles by the spindle fibers of the cell is called the Anaphase stage. It is a stage of mitosis or meiosis after the process of metaphase.
Additional Information: -Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
-There are two distinct types of cell division:
(a)A vegetative division, where each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell (mitosis)
(b)A reproductive division, where the number of chromosomes is reduced to half in the daughter cells to produce haploid gametes (meiosis).
-Anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the chromosomes are segregated to opposite poles of the cell.
-Anaphase starts after the cell passes the spindle formation checkpoint, which allows chromosomes or chromatids to separate.
-In meiosis the Anaphase is divided into two stages: Anaphase I and Anaphase II.
So, the correct answer is ‘Anaphase’.

Note: Cell division consists of various stages: Prophase – first stage of division. Chromatin threads condense to form shorter more visible strands called chromosomes. Metaphase – chromosomes arrange themselves on the metaphase plate in the middle of the cell. Anaphase – very short stage of the cell, the chromosomes split and the sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell. Telophase – last stage of the cell cycle, separation of daughter cells by formation of the cell plate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




