
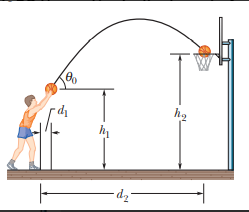
At what initial speed must the basketball player in fig throw the ball, at angle ${{\theta }_{0}}={{55}^{0}}$ above the horizontal, to make the foul shot? The horizontal distances are ${{d}_{1}}=1.0ft$ and ${{d}_{2}}=14ft$ , and the heights are ${{h}_{1}}=7.0ft$ and ${{h}_{2}}=10ft$.

Answer
511.5k+ views
Hint: Speed is defined as the distance covered per unit time and speed is a scalar quantity. SI unit of speed is $m{{s}^{-1}}$. Displacement is defined as the process in which objects' positions are changed and in displacement the initial position of objects are changed. Displacement is also defined as change in initial position of objects to the final position and displacement is denoted as S.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Displacement is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction and displacement is measured in terms of meters. The dimensional formula of displacement is ${{M}^{0}}{{L}^{1}}{{T}^{0}}$ and displacement plays a very important role while determining velocity (v). Velocity is also a vector quantity.
Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement with respect to time and in kinematics velocity is a fundamental concept. SI unit of velocity is $m{{s}^{-1}}$ and velocity tracking is the measure of velocity.
Velocity (v) =$\dfrac{\Delta S}{\Delta t}$
The dimensional formula of velocity is ${{M}^{0}}{{L}^{1}}{{T}^{-1}}$.
The force which causes a change in velocity and change in velocity creates a force.
We know that
${{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{x}{\cos {{\theta }_{0}}}\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{2(x\tan {{\theta }_{0}}-y)}}$ $\cdots \cdots (1)$
From the data $g=32ft{{s}^{-2}}$, $x=13ft$, $y=3ft$ and ${{\theta }_{0}}={{55}^{0}}$
Substituting these values in equation (1)
${{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{13}{\cos {{55}^{0}}}\sqrt{\dfrac{32}{2(13\tan {{55}^{0}}-3)}}$
We get ${{v}_{0}}=23ft{{s}^{-1}}$
Note: Acceleration depends on the mass and also on the force. The force velocity, acceleration and momentum have both magnitude and a direction. Heavier objects have less acceleration compared to lighter objects. Newton’s second law of motion to relate the motion of the object to the forces involved. Objects with constant masses are used in Newton’s second law.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Displacement is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction and displacement is measured in terms of meters. The dimensional formula of displacement is ${{M}^{0}}{{L}^{1}}{{T}^{0}}$ and displacement plays a very important role while determining velocity (v). Velocity is also a vector quantity.
Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement with respect to time and in kinematics velocity is a fundamental concept. SI unit of velocity is $m{{s}^{-1}}$ and velocity tracking is the measure of velocity.
Velocity (v) =$\dfrac{\Delta S}{\Delta t}$
The dimensional formula of velocity is ${{M}^{0}}{{L}^{1}}{{T}^{-1}}$.
The force which causes a change in velocity and change in velocity creates a force.
We know that
${{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{x}{\cos {{\theta }_{0}}}\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{2(x\tan {{\theta }_{0}}-y)}}$ $\cdots \cdots (1)$
From the data $g=32ft{{s}^{-2}}$, $x=13ft$, $y=3ft$ and ${{\theta }_{0}}={{55}^{0}}$
Substituting these values in equation (1)
${{v}_{0}}=\dfrac{13}{\cos {{55}^{0}}}\sqrt{\dfrac{32}{2(13\tan {{55}^{0}}-3)}}$
We get ${{v}_{0}}=23ft{{s}^{-1}}$
Note: Acceleration depends on the mass and also on the force. The force velocity, acceleration and momentum have both magnitude and a direction. Heavier objects have less acceleration compared to lighter objects. Newton’s second law of motion to relate the motion of the object to the forces involved. Objects with constant masses are used in Newton’s second law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




