
At a distance 2h from the foot of a tower of height h, the tower and a pole at the top of the tower subtend equal angles. Height of the pole should be
A.\[\dfrac{5H}{3}\ m\]
B.\[\dfrac{4H}{3}\ m\]
C.\[\dfrac{7H}{5}\ m\]
D.\[\dfrac{3H}{2}\ m\]
Answer
617.1k+ views
HINT:The formula for writing tangent of an angle is
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}\] .
We would also use the formula for tangent of twice the angle to evaluate the answer in this question as follows
\[\tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }\]
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned in the question, the figure would look like the below picture
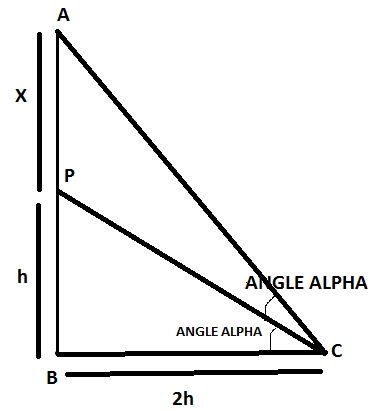
Now, on analyzing the figure above, we get to the equation as follows
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta ABC, \\
& \tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha } \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let the height of the pole be X. hence, we can write, using the formula mentioned in the hint, as follows
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta ABC, \\
& \tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\ \ \ \ \ ...(a) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on similar grounds, we can write as
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta PBC, \\
& \tan \alpha =\dfrac{H}{2H} \\
& \tan \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2}\ \ \ \ \ ...(b) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, using the property mentioned in the hint, we can simplify equation (a) as follows
\[\tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }=\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\]
On using the value from equation (b), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}}{1-\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\ \ \ \ \ ...(c) \\
& 3X+3H=8H \\
& X=\dfrac{5H}{3}\ m \\
\end{align}\]
(On cross multiplying at step (c))
Hence, the height of the pole is \[\dfrac{5H}{3}\ m\] .
NOTE:The figure in this question is very tricky and is difficult to visualize it at first. Hence, the students can make an error while drawing the figure and then end up making a mistake and they would get to the correct solution.
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}\] .
We would also use the formula for tangent of twice the angle to evaluate the answer in this question as follows
\[\tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }\]
Complete step by step answer:
As mentioned in the question, the figure would look like the below picture

Now, on analyzing the figure above, we get to the equation as follows
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta ABC, \\
& \tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha } \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let the height of the pole be X. hence, we can write, using the formula mentioned in the hint, as follows
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta ABC, \\
& \tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\ \ \ \ \ ...(a) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, on similar grounds, we can write as
\[\begin{align}
& In\ \Delta PBC, \\
& \tan \alpha =\dfrac{H}{2H} \\
& \tan \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2}\ \ \ \ \ ...(b) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, using the property mentioned in the hint, we can simplify equation (a) as follows
\[\tan 2\alpha =\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }=\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\]
On using the value from equation (b), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \alpha }{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\alpha }=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}}{1-\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H} \\
& \dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{X+H}{2H}\ \ \ \ \ ...(c) \\
& 3X+3H=8H \\
& X=\dfrac{5H}{3}\ m \\
\end{align}\]
(On cross multiplying at step (c))
Hence, the height of the pole is \[\dfrac{5H}{3}\ m\] .
NOTE:The figure in this question is very tricky and is difficult to visualize it at first. Hence, the students can make an error while drawing the figure and then end up making a mistake and they would get to the correct solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




