
Assertion:-Mountain roads rarely go straight up the slope.
Reason:- Slope of mountains are large, therefore more chances of vehicles to slip from roads.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer
564k+ views
Hint: To check whether the statement and the reason are correct, assume a body moving up a mountain. To understand better, draw a diagram of a body moving up the mountain along a straight road and assign the forces acting on the body then try to find the relation between slope and frictional force acting on the body. Use this relation to know whether the statement and the reason given is correct or incorrect.
Complete answer:
Given an assertion, mountain roads rarely go straight up the slope.And the reason, slope of mountains are large, therefore more chances for vehicles to slip from roads.First let’s understand why mountains rarely have straight roads.We observe that in mountains, the roads are not straight up they are mostly in the zigzag form that is with many turns or curves. To understand the reason behind this, let us take a body of mass \[m\] moving up a mountain. Let us draw a diagram of the body moving up through a straight road AB on a mountain by assigning the forces acting on the body.
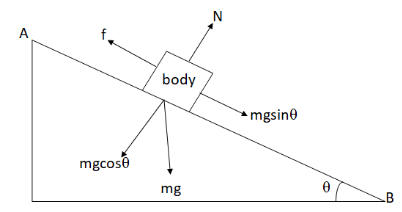
In the diagram above, \[f\] is the frictional force acting opposite to the sliding direction, \[N\] is the normal reaction and \[\theta \] is the inclination of the mountain. Larger the value of \[\theta \], larger is the slope of the mountain.
The body is in motion, so the friction here will be kinetic friction and we know kinetic friction is equal to
\[f = {\mu _k}N\] ……………....(i)
where \[{\mu _k}\] is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
From the figure, we observe that \[N = mg\cos \theta \], putting this value in equation (i), we get
\[f = {\mu _k}mg\cos \theta \]
From the equation above we observe that the quantity \[{\mu _k}mg\] is constant so,
\[f \propto \cos \theta \]
As \[\theta \] increases the value of \[\cos \theta \] decreases that is the kinetic friction \[f\] decreases or we can say with increase in slope of the mountain the frictional force decreases that is there is risk of sliding down. Therefore, mountain roads rarely go straight up the slope because slopes of mountains are large, so there are more chances for vehicles to slip from roads.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Here, we have discussed kinetic friction. There is one more type of friction known as static friction. Static friction is a type of friction which keeps a body at rest, for example if a vehicle is parked on a hill in this case there will be static friction. Also, remember static friction is greater than kinetic friction.
Complete answer:
Given an assertion, mountain roads rarely go straight up the slope.And the reason, slope of mountains are large, therefore more chances for vehicles to slip from roads.First let’s understand why mountains rarely have straight roads.We observe that in mountains, the roads are not straight up they are mostly in the zigzag form that is with many turns or curves. To understand the reason behind this, let us take a body of mass \[m\] moving up a mountain. Let us draw a diagram of the body moving up through a straight road AB on a mountain by assigning the forces acting on the body.

In the diagram above, \[f\] is the frictional force acting opposite to the sliding direction, \[N\] is the normal reaction and \[\theta \] is the inclination of the mountain. Larger the value of \[\theta \], larger is the slope of the mountain.
The body is in motion, so the friction here will be kinetic friction and we know kinetic friction is equal to
\[f = {\mu _k}N\] ……………....(i)
where \[{\mu _k}\] is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
From the figure, we observe that \[N = mg\cos \theta \], putting this value in equation (i), we get
\[f = {\mu _k}mg\cos \theta \]
From the equation above we observe that the quantity \[{\mu _k}mg\] is constant so,
\[f \propto \cos \theta \]
As \[\theta \] increases the value of \[\cos \theta \] decreases that is the kinetic friction \[f\] decreases or we can say with increase in slope of the mountain the frictional force decreases that is there is risk of sliding down. Therefore, mountain roads rarely go straight up the slope because slopes of mountains are large, so there are more chances for vehicles to slip from roads.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: Here, we have discussed kinetic friction. There is one more type of friction known as static friction. Static friction is a type of friction which keeps a body at rest, for example if a vehicle is parked on a hill in this case there will be static friction. Also, remember static friction is greater than kinetic friction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




