
Assertion
A saturated solution of $\,KCl\,$ is used in making salt bridges.
Reason
Ionic mobilities of $\,{K^ + }\,$ and $\,C{l^ - }\,$ are the same.
A.Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
B.Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
C.Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
D.Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The salt bridge normally consists of a solid electrolyte that is often made up of ions. A salt bridge is used on the electrodes to prevent charges from accumulating. In a galvanic cell, such as a voltaic cell or Daniel cell, salt bridges are commonly used.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first learn about the functions of salt bridge;
A salt bridge is a link comprising a weak electrolyte between the oxidation and reduction half-cells in a galvanic cell. Its goal is to prevent the electrochemical response from hitting balance very fast. One solution would accumulate positive charge quickly, while the other would accumulate negative charge, if a cell is built without a salt bridge. This will interrupt the response and therefore the output of electricity.
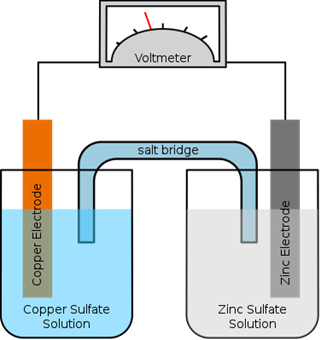
The $\,KCl\,$ or $\,KN{O_3}\,$ or $\,N{H_4}N{O_3}\,$ solution serves as an inert electrolyte. The cations and anions of the electrolyte used should be of the same ionic mobility. The electrolyte should be inert.
So, among the conditions of a salt bridge is the anion and cation having equal mobilities.
Ionic mobilities of the anions and cations in $\,KCl\,$ salt bridge are as follows;
$\,{K^ + } \geqslant 7.60\,{m^2}{S^{ - 1}}{V^{ - 1}}\,$
$\,C{l^ - } \geqslant 7.92{m^2}{S^{ - 1}}{V^{ - 1}}\,$
From all the above explanations, it is clear that both the assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
So, option A is the correct answer for this question.
Note:
The aim of a salt bridge is not to transfer electrons from the electrolyte; rather, since the electrons move from one half of the cell to the other, it is to preserve charge equilibrium. Basically, it preserves electrical neutrality inside the internal circuit and prevents the cell from easily performing its equilibrium response.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first learn about the functions of salt bridge;
A salt bridge is a link comprising a weak electrolyte between the oxidation and reduction half-cells in a galvanic cell. Its goal is to prevent the electrochemical response from hitting balance very fast. One solution would accumulate positive charge quickly, while the other would accumulate negative charge, if a cell is built without a salt bridge. This will interrupt the response and therefore the output of electricity.

The $\,KCl\,$ or $\,KN{O_3}\,$ or $\,N{H_4}N{O_3}\,$ solution serves as an inert electrolyte. The cations and anions of the electrolyte used should be of the same ionic mobility. The electrolyte should be inert.
So, among the conditions of a salt bridge is the anion and cation having equal mobilities.
Ionic mobilities of the anions and cations in $\,KCl\,$ salt bridge are as follows;
$\,{K^ + } \geqslant 7.60\,{m^2}{S^{ - 1}}{V^{ - 1}}\,$
$\,C{l^ - } \geqslant 7.92{m^2}{S^{ - 1}}{V^{ - 1}}\,$
From all the above explanations, it is clear that both the assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
So, option A is the correct answer for this question.
Note:
The aim of a salt bridge is not to transfer electrons from the electrolyte; rather, since the electrons move from one half of the cell to the other, it is to preserve charge equilibrium. Basically, it preserves electrical neutrality inside the internal circuit and prevents the cell from easily performing its equilibrium response.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




