
As shown in the figure, one block of $ 2.0kg $ at one end and the other of $ 3.0kg $ at the other end of a light string are connected. If this system remains stationary, find the magnitude and direction of the frictional force.
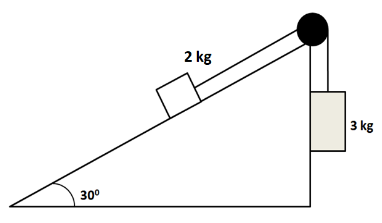
(A) $ 20N $ , downward on slope
(B) $ 20N $ , upward on slope
(C) $ 10N $ , downward on slope
(D) $ 10N $ , upward on slope

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to apply the conditions of equilibrium on each of the two blocks given in this question to get the equations of translational equilibrium. On solving these equations we will get the final answer.
Complete step-by-step solution
As can be seen in the above figure, a block of $ 3.0kg $ is attached to the block of $ 2.0kg $ through a string. So it will try to pull the $ 2.0kg $ block upward the slope. But the component of weight of the $ 2.0kg $ block will try to pull it downward on the slope. Since the $ 3.0kg $ block is heavier than the $ 2.0kg $ block, so the block will have a tendency to slide upward the slope of the inclined plane. So the friction will act downward on the $ 2.0kg $ block. So we can show the different forces acting on the $ 2.0kg $ block as shown in the below diagram
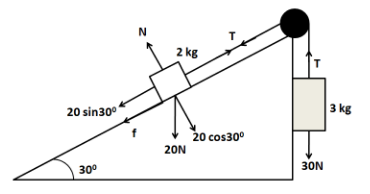
According to the question, the system remains stationary. This means that both the $ 2.0kg $ and the $ 3.0kg $ blocks must be in equilibrium. Considering the equilibrium of the $ 3.0kg $ block, we have
$ T = 30{\text{ N}} $ .....................(1)
Now, we consider the equilibrium if the $ 2.0kg $ block in the direction normal to the incline to get
$ N = 20\cos {30^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow N = 10\sqrt 3 {\text{ N}} $
Similarly considering the equilibrium of the block in the direction parallel to the incline, we have
$ T = 20\sin {30^ \circ } + f $
$ \Rightarrow T = 10 + f $
Putting (1) in the above equation, we get
$ 30 = 10 + f $
$ \Rightarrow f = 20{\text{ N}} $
Thus, the frictional force of $ 20N $ acts downwards the slope.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note
There was no need to calculate the normal reaction on the $ 2.0kg $ block. This is because we were supposed to calculate the frictional force itself, which is easily calculated by the equations of the equilibrium.
Complete step-by-step solution
As can be seen in the above figure, a block of $ 3.0kg $ is attached to the block of $ 2.0kg $ through a string. So it will try to pull the $ 2.0kg $ block upward the slope. But the component of weight of the $ 2.0kg $ block will try to pull it downward on the slope. Since the $ 3.0kg $ block is heavier than the $ 2.0kg $ block, so the block will have a tendency to slide upward the slope of the inclined plane. So the friction will act downward on the $ 2.0kg $ block. So we can show the different forces acting on the $ 2.0kg $ block as shown in the below diagram

According to the question, the system remains stationary. This means that both the $ 2.0kg $ and the $ 3.0kg $ blocks must be in equilibrium. Considering the equilibrium of the $ 3.0kg $ block, we have
$ T = 30{\text{ N}} $ .....................(1)
Now, we consider the equilibrium if the $ 2.0kg $ block in the direction normal to the incline to get
$ N = 20\cos {30^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow N = 10\sqrt 3 {\text{ N}} $
Similarly considering the equilibrium of the block in the direction parallel to the incline, we have
$ T = 20\sin {30^ \circ } + f $
$ \Rightarrow T = 10 + f $
Putting (1) in the above equation, we get
$ 30 = 10 + f $
$ \Rightarrow f = 20{\text{ N}} $
Thus, the frictional force of $ 20N $ acts downwards the slope.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note
There was no need to calculate the normal reaction on the $ 2.0kg $ block. This is because we were supposed to calculate the frictional force itself, which is easily calculated by the equations of the equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




