
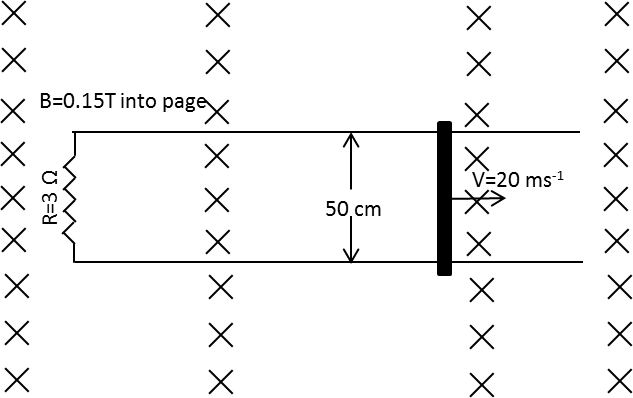
As shown in the figure, a metal rod makes contact with a partial circuit and completes the circuit. The circuit area is perpendicular to a magnetic field with \[B = 0.15\,{\text{T}}\]. If the resistance out of the total circuit is \[3\,\Omega \], the force needed to move the rod as indicated with a constant speed of \[2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] will be equal to
A. \[3.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\]
B. \[2.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\]
C. \[6.57 \times {10^{ - 4}}\]
D. \[4.36 \times {10^{ - 4}}\]

Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Use the formulae for the induced emf in the rod, induced current in the rod and the force on the rod moving in the magnetic field. These formulae give the relation between the force on the rod, emf induced, current induced and total resistance.
Formula used:
The emf \[e\] induced in the moving rod is
\[e = BLv\] …… (1)
Here, \[B\] is the magnetic field, \[L\] is the length of the moving rod and \[v\] is the speed of the moving rod.
The current induced \[I\] in a rod moving in the magnetic field is
\[I = \dfrac{e}{R}\] …… (2)
Here, \[e\] is the emf induced in the rod and \[R\] is the resistance.
The force \[F\] required to move a rod in the magnetic field is
\[F = ILB\sin \theta \] …… (3)
Here, \[I\] is the current induced in the rod, \[L\] is the length of the rod, \[B\] is the magnetic field and \[\theta \] is the angle between the current and magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
A rod of length \[50\,{\text{cm}}\] is moving in the magnetic field of \[0.15\,{\text{T}}\] with a speed \[2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]. The total resistance of the circuit is \[3\,\Omega \] and the direction of the magnetic field is into the page.
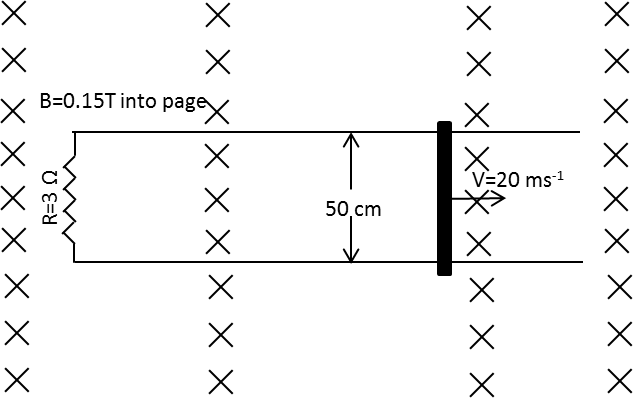
Due to the induced emf, the direction of the induced current in the rod is in the anti-clockwise direction.
Calculate the current induced \[I\] in the rod.
Substitute \[BLv\] for \[e\] in equation (2).
\[I = \dfrac{{BLv}}{R}\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{BLv}}{R}\] for \[I\] in equation (3).
\[F = \dfrac{{BLv}}{R}LB\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{{B^2}{L^2}v\sin \theta }}{R}\]
Since the current is in the anti-clockwise direction, the angle between the induced current and the magnetic field is \[90^\circ \].
Substitute \[0.15\,{\text{T}}\] for \[B\], \[50\,{\text{cm}}\] for \[L\],\[2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] for \[v\], \[90^\circ \] for \[\theta \] and \[3\,\Omega \] for \[R\] in equation (1).
\[F = \dfrac{{{{\left( {0.15\,{\text{T}}} \right)}^2}{{\left( {50\,{\text{cm}}} \right)}^2}\left( {2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\sin 90^\circ }}{{3\,\Omega }}\]
\[F = \dfrac{{{{\left( {0.15\,{\text{T}}} \right)}^2}{{\left[ {\left( {50\,{\text{cm}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 2}}\,{\text{m}}}}{{1\,{\text{cm}}}}} \right)} \right]}^2}\left( {2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\sin 90^\circ }}{{3\,\Omega }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 37.5 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,{\text{N}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 3.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{N}}\]
Therefore, the force needed to move the rod is \[3.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{N}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
According to Fleming’s left hand rule, the rod is required to move the rod in the right direction.
Due to the induced emf, the direction of the induced current in the rod is in the anti-clockwise direction.
Formula used:
The emf \[e\] induced in the moving rod is
\[e = BLv\] …… (1)
Here, \[B\] is the magnetic field, \[L\] is the length of the moving rod and \[v\] is the speed of the moving rod.
The current induced \[I\] in a rod moving in the magnetic field is
\[I = \dfrac{e}{R}\] …… (2)
Here, \[e\] is the emf induced in the rod and \[R\] is the resistance.
The force \[F\] required to move a rod in the magnetic field is
\[F = ILB\sin \theta \] …… (3)
Here, \[I\] is the current induced in the rod, \[L\] is the length of the rod, \[B\] is the magnetic field and \[\theta \] is the angle between the current and magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
A rod of length \[50\,{\text{cm}}\] is moving in the magnetic field of \[0.15\,{\text{T}}\] with a speed \[2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]. The total resistance of the circuit is \[3\,\Omega \] and the direction of the magnetic field is into the page.

Due to the induced emf, the direction of the induced current in the rod is in the anti-clockwise direction.
Calculate the current induced \[I\] in the rod.
Substitute \[BLv\] for \[e\] in equation (2).
\[I = \dfrac{{BLv}}{R}\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{BLv}}{R}\] for \[I\] in equation (3).
\[F = \dfrac{{BLv}}{R}LB\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{{B^2}{L^2}v\sin \theta }}{R}\]
Since the current is in the anti-clockwise direction, the angle between the induced current and the magnetic field is \[90^\circ \].
Substitute \[0.15\,{\text{T}}\] for \[B\], \[50\,{\text{cm}}\] for \[L\],\[2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] for \[v\], \[90^\circ \] for \[\theta \] and \[3\,\Omega \] for \[R\] in equation (1).
\[F = \dfrac{{{{\left( {0.15\,{\text{T}}} \right)}^2}{{\left( {50\,{\text{cm}}} \right)}^2}\left( {2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\sin 90^\circ }}{{3\,\Omega }}\]
\[F = \dfrac{{{{\left( {0.15\,{\text{T}}} \right)}^2}{{\left[ {\left( {50\,{\text{cm}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 2}}\,{\text{m}}}}{{1\,{\text{cm}}}}} \right)} \right]}^2}\left( {2\,{\text{m}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}} \right)\sin 90^\circ }}{{3\,\Omega }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 37.5 \times {10^{ - 4}}\,{\text{N}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 3.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{N}}\]
Therefore, the force needed to move the rod is \[3.75 \times {10^{ - 3}}\,{\text{N}}\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
According to Fleming’s left hand rule, the rod is required to move the rod in the right direction.
Due to the induced emf, the direction of the induced current in the rod is in the anti-clockwise direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




