
: As per this diagram a point charge $ + q$ is placed at the origin O. Work done in taking another point charge $ - Q$ from the point A [coordinates $(0,a)$] to another point B [coordinates $(a,0)$] along the straight path AB is,
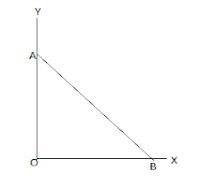
$A.$ Zero
$
B.\;\left( {\dfrac{{ - qQ}}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)\sqrt 2 a \\
C.\;{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{{qQ}}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \cdot \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
D.\;{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{{qQ}}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) \cdot \sqrt 2 a \\
$
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The electric potential energy is the energy which results from the conservative coulomb forces and which is associated with the configuration of the particular set of point charges within the defined system. It is also known as the electrostatic potential energy and is measured in joules.
Complete step by step answer:
In an electric field, let us consider that there are two charges ${q_1}{\text{ and }}{{\text{q}}_2}$ which are placed at the distance ${r_{1{\text{ }}}}and{\text{ }}{{\text{r}}_2}$ respectively.
Then the potential energy of two charge system is $U = \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{4\pi { \in _0}{r_{12}}}}$
Where ${r_{12}}$ is the distance between the two electric charges.
When the charge $ - Q$ at the point A, the potential energy ${U_A} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(OA)}}$
${U_A} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}{\text{}}.....{\text{ (1)}}$
When the charge $ - Q$ at the point B, the potential energy ${U_B} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(OB)}}$
${U_B} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}{\text{}}.....{\text{ (2)}}$
Work done, ${W_{AB}} = {U_B} - {U_A}$
Place the values in the above equations by using the equations $(1){\text{ and (2)}}$
${W_{AB}} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}} - \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}$
Minus between two the same terms gives the resultant value zero.
$\therefore{W_{AB}} = 0$
Therefore, work done is zero.
Hence, from the given multiple choices – the option A is the correct answer.
Note: In physics, the charge is the physical property of the matter which causes force when placed in an electro-magnetic field. Charge is also known as the electric charge, the electrical charge or the electrostatic charge and is symbolized as “q” and is measured in coulomb.Remember the basic concepts and formulas to solve these types of questions.
Complete step by step answer:
In an electric field, let us consider that there are two charges ${q_1}{\text{ and }}{{\text{q}}_2}$ which are placed at the distance ${r_{1{\text{ }}}}and{\text{ }}{{\text{r}}_2}$ respectively.
Then the potential energy of two charge system is $U = \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{4\pi { \in _0}{r_{12}}}}$
Where ${r_{12}}$ is the distance between the two electric charges.
When the charge $ - Q$ at the point A, the potential energy ${U_A} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(OA)}}$
${U_A} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}{\text{}}.....{\text{ (1)}}$
When the charge $ - Q$ at the point B, the potential energy ${U_B} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(OB)}}$
${U_B} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}{\text{}}.....{\text{ (2)}}$
Work done, ${W_{AB}} = {U_B} - {U_A}$
Place the values in the above equations by using the equations $(1){\text{ and (2)}}$
${W_{AB}} = \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}} - \dfrac{{( - Q)q}}{{4\pi { \in _0}(a)}}$
Minus between two the same terms gives the resultant value zero.
$\therefore{W_{AB}} = 0$
Therefore, work done is zero.
Hence, from the given multiple choices – the option A is the correct answer.
Note: In physics, the charge is the physical property of the matter which causes force when placed in an electro-magnetic field. Charge is also known as the electric charge, the electrical charge or the electrostatic charge and is symbolized as “q” and is measured in coulomb.Remember the basic concepts and formulas to solve these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




