
Arrange the given structures in the correct sequence of pathways of light from outside to inside the eyeball of the human eye.
(A) Lens
(B) Aqueous humour
(C) Vitreous humour
(D) Cornea
Choose the correct sequence.
A) D, B, A, C
B) A, B, C, D
C) D, C, B, A
D) A, D, B, C
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: The eye is one of the most important and complex sense organs that we humans have. It aids in the visualization of objects, as well as light, color, and depth perception. Furthermore, these sense organs are similar to cameras in that they assist us in seeing objects when light from the outside enters them.
Complete answer:
A human eye has a diameter of about 2.3 cm and is almost a spherical ball filled with fluid. It is made up of the following sections:
Sclera: The sclera is the protective tough white layer that covers the outside of the eye (white part of the eye).
Cornea: The cornea is the transparent front part of the sclera. The cornea allows light to enter the eye.
Iris: The iris is a dark muscular tissue and ring-like structure that lies behind the cornea. The eye's color is determined by the color of the iris. By adjusting the iris, the iris also helps to regulate or adjust exposure.
Pupil: The pupil is a small opening in the iris. The size of it is controlled by the iris. It regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
lens: A transparent structure called a lens is located behind the pupil. It changes shape to focus light on the retina thanks to the action of ciliary muscles. When focusing on distant objects, it becomes thinner, and when focusing on nearby objects, it becomes thicker.
retina: The retina is a light-sensitive layer made up of many nerve cells. It converts the lens' images into electrical impulses. Through the optic nerves, these electrical impulses are then transmitted to the brain.
Optic nerves: Optic nerves are divided into two types. Cones and rods are examples of these.
The cornea bends light, which then passes through the anterior chamber, the aqueous, and the pupil before being refracted by the lens, which then passes through the vitreous and focuses on the retina.
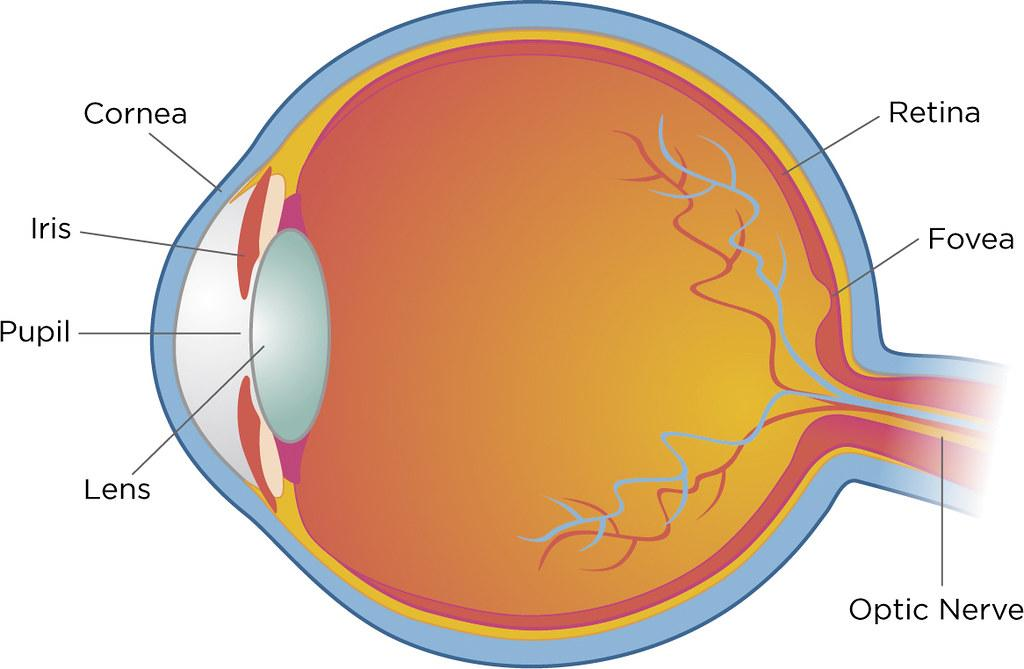
Thus, the answer is option A: D, B, A, C.
Note: There are six muscles in the eye. The medial rectus, lateral rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, and superior oblique are all included in this group. These muscles' primary function is to provide various tensions and torques that help to control eye movement.
Complete answer:
A human eye has a diameter of about 2.3 cm and is almost a spherical ball filled with fluid. It is made up of the following sections:
Sclera: The sclera is the protective tough white layer that covers the outside of the eye (white part of the eye).
Cornea: The cornea is the transparent front part of the sclera. The cornea allows light to enter the eye.
Iris: The iris is a dark muscular tissue and ring-like structure that lies behind the cornea. The eye's color is determined by the color of the iris. By adjusting the iris, the iris also helps to regulate or adjust exposure.
Pupil: The pupil is a small opening in the iris. The size of it is controlled by the iris. It regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
lens: A transparent structure called a lens is located behind the pupil. It changes shape to focus light on the retina thanks to the action of ciliary muscles. When focusing on distant objects, it becomes thinner, and when focusing on nearby objects, it becomes thicker.
retina: The retina is a light-sensitive layer made up of many nerve cells. It converts the lens' images into electrical impulses. Through the optic nerves, these electrical impulses are then transmitted to the brain.
Optic nerves: Optic nerves are divided into two types. Cones and rods are examples of these.
The cornea bends light, which then passes through the anterior chamber, the aqueous, and the pupil before being refracted by the lens, which then passes through the vitreous and focuses on the retina.

Thus, the answer is option A: D, B, A, C.
Note: There are six muscles in the eye. The medial rectus, lateral rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, and superior oblique are all included in this group. These muscles' primary function is to provide various tensions and torques that help to control eye movement.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




