
Arrange the following in order of decreasing boiling point:
(I) n-Butane (II) n-Butanol (III) n-Butyl chloride (IV) Isobutane
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint:Alcohols and alkyl halides have higher boiling point than alkanes. Straight chain alkanes have higher boiling point than branched chain alkanes.
Complete answer:
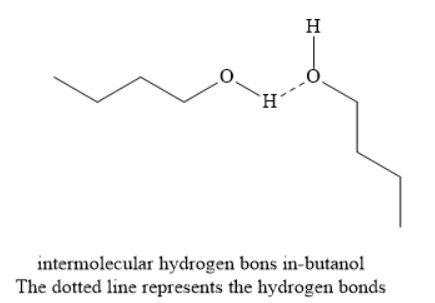
n-Butanol is an alcohol and contains hydroxyl functional groups. Hydrogen atoms are attached to electronegative oxygen atoms. Due to this, intermolecular hydrogen bonds are formed in butanol molecules. This leads to molecular association and high energy is needed to break these intermolecular hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds is not possible in case of n-butane, isobutane and n-butyl chloride. Hence, the boiling point of butanol is highest among the given compounds.
n-butyl chloride is an alkyl halide. It is a polar compound as it contains polar carbon-chlorine bonds and has non zero dipole moment. Due to this, dipole-dipole forces of attraction are present between molecules of n-butyl chloride. This increases the boiling point. Hence, n-butyl chloride has higher boiling point than n-butane and isobutane,
n-butane is straight chain hydrocarbon whereas isobutane is branched chain hydrocarbon. The van der waals forces in straight chain hydrocarbons are stronger than those in branched chain hydrocarbons. Hence, n-butane has higher boiling point than isobutane.
Hence, the decreasing order of the boiling points of the given compounds is n-butanol> n-butyl chloride > n-butane > isobutane.
Note:
The formation of hydrogen bonds is possible when hydrogen atom is attached to electronegative nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atom. If a hydrogen atom is not attached to electronegative nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atom, then hydrogen bonds will not be formed.
Complete answer:
n-Butanol is an alcohol and contains hydroxyl functional groups. Hydrogen atoms are attached to electronegative oxygen atoms. Due to this, intermolecular hydrogen bonds are formed in butanol molecules. This leads to molecular association and high energy is needed to break these intermolecular hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds is not possible in case of n-butane, isobutane and n-butyl chloride. Hence, the boiling point of butanol is highest among the given compounds.
n-butyl chloride is an alkyl halide. It is a polar compound as it contains polar carbon-chlorine bonds and has non zero dipole moment. Due to this, dipole-dipole forces of attraction are present between molecules of n-butyl chloride. This increases the boiling point. Hence, n-butyl chloride has higher boiling point than n-butane and isobutane,
n-butane is straight chain hydrocarbon whereas isobutane is branched chain hydrocarbon. The van der waals forces in straight chain hydrocarbons are stronger than those in branched chain hydrocarbons. Hence, n-butane has higher boiling point than isobutane.


Hence, the decreasing order of the boiling points of the given compounds is n-butanol> n-butyl chloride > n-butane > isobutane.
Note:
The formation of hydrogen bonds is possible when hydrogen atom is attached to electronegative nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atom. If a hydrogen atom is not attached to electronegative nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine atom, then hydrogen bonds will not be formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




