
Arrange the following carbanions in increasing order of their stability.

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Stability of carbanions decreases as we are moving from primary to tertiary carbanion. Because of the +I effect, the methyl groups increase the intensity of the negative charge on central carbon in tertiary carbanion which makes tertiary carbanion more unstable.
Complete step by step answer:
- The stability of carbanions is as follows.
Primary carbanion > secondary carbanion > tertiary carbanion.
- As per the above order we can say that primary carbanion is more stable then secondary and tertiary carbanion.
- Due to +I effect tertiary carbanion is less stable than secondary and primary carbanions.
- Due to the presence of – I affect the stability of the carbanions increases.
- If molecules (carbanions) contain electron withdrawing groups, they withdraw the electrons from the carbanions and make the carbanions more stable. This effect is called –I effect.
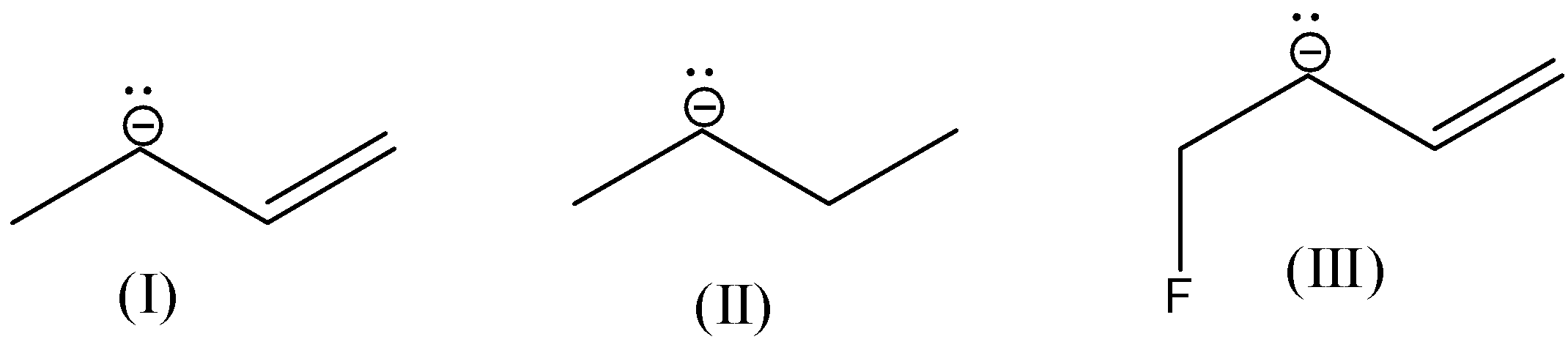
- In the question there are three molecules having carbanions in their structures. They are as follows.
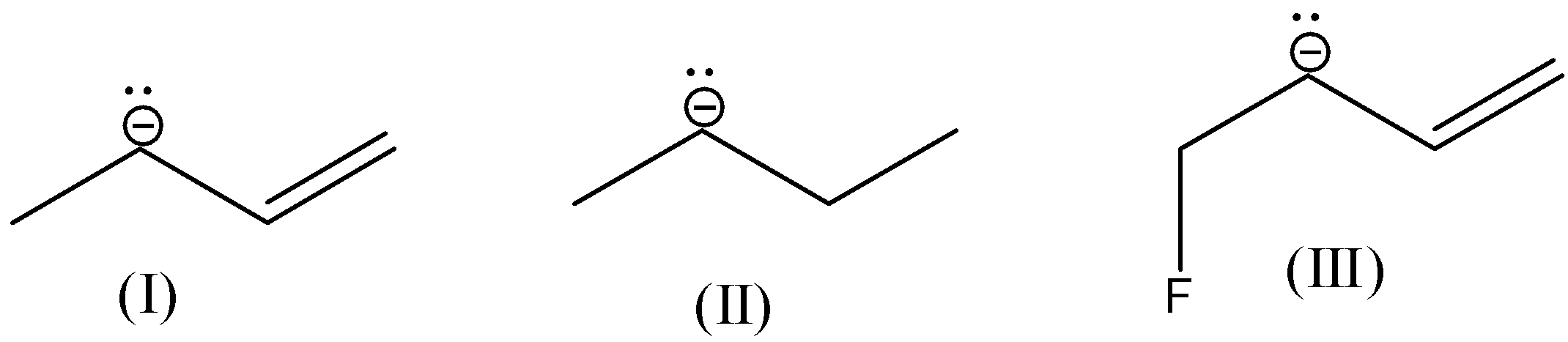
- All the given molecules contain primary carbanions.
- The molecule-I contains primary carbanion adjacent to a double bond.
- The molecule-I shows resonance as follows.
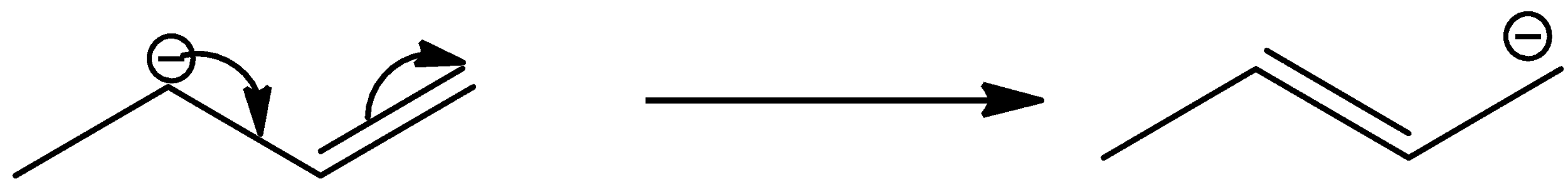
- But still molecule-I is unstable because a large amount of electrons creates high repulsions.
- Coming to the molecule-II, it contains only primary carbanion. There are no – I groups and no double bond in it. Then it is more stable than molecule-I.
- In molecule-III there is a presence of fluorine (an electron withdrawing group) makes molecule-III more stable due to – I effect.
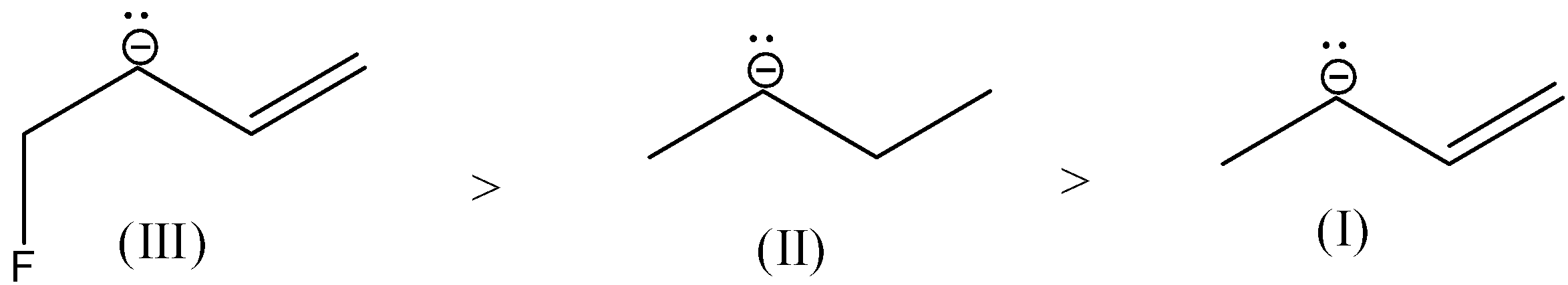
- Therefore the increasing order of the stability of the given carbanions is as follows.
Note: If there is a presence of any electron donating groups (+I effect) in carbanions then the carbanions are more unstable than the normal carbanions. The stability of the carbanions will increase by the presence of electron withdrawing groups.
Complete step by step answer:
- The stability of carbanions is as follows.
Primary carbanion > secondary carbanion > tertiary carbanion.
- As per the above order we can say that primary carbanion is more stable then secondary and tertiary carbanion.
- Due to +I effect tertiary carbanion is less stable than secondary and primary carbanions.
- Due to the presence of – I affect the stability of the carbanions increases.
- If molecules (carbanions) contain electron withdrawing groups, they withdraw the electrons from the carbanions and make the carbanions more stable. This effect is called –I effect.
- In the question there are three molecules having carbanions in their structures. They are as follows.

- All the given molecules contain primary carbanions.
- The molecule-I contains primary carbanion adjacent to a double bond.
- The molecule-I shows resonance as follows.
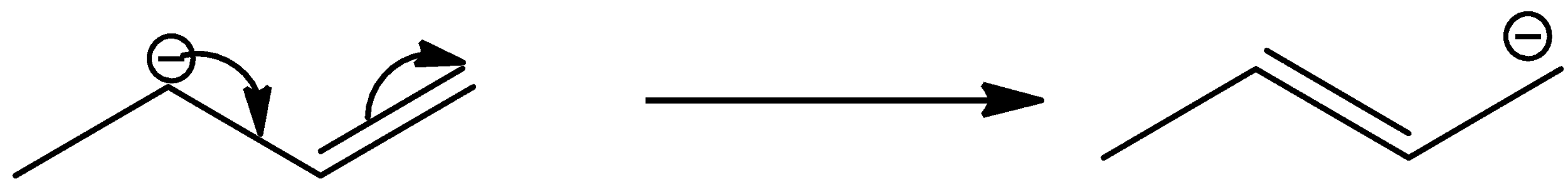
- But still molecule-I is unstable because a large amount of electrons creates high repulsions.
- Coming to the molecule-II, it contains only primary carbanion. There are no – I groups and no double bond in it. Then it is more stable than molecule-I.
- In molecule-III there is a presence of fluorine (an electron withdrawing group) makes molecule-III more stable due to – I effect.
- Therefore the increasing order of the stability of the given carbanions is as follows.

Note: If there is a presence of any electron donating groups (+I effect) in carbanions then the carbanions are more unstable than the normal carbanions. The stability of the carbanions will increase by the presence of electron withdrawing groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




