
What is the area of a right angled isosceles triangle whose hypotenuse is $6\sqrt 2 $cm?
$
(a){\text{ 12c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
(b){\text{ 18c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
(c){\text{ 24c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
(d){\text{ 36c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
$
Answer
627k+ views
Hint: In this question put side AB=BC because it is a isosceles triangle and equate it to some variable, then use Pythagoras theorem which is ${\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2}$ to get the variable and then the area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
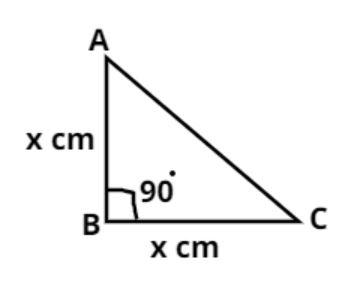
As we know in an isosceles triangle two sides are equal.
Now the given isosceles triangle is a right angle triangle. Therefore its base and perpendicular are equal as shown in figure.
Let its base and perpendicular be x cm.
Now it is given that its hypotenuse is AC = $6\sqrt 2 $ cm.
So apply Pythagoras theorem in right triangle we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} =
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2} = {\left( {6\sqrt 2 } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 72$
Now divide by 2 we have,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{72}}{2} = 36 = {6^2}\]
Therefore x = 6 cm.
Now as we know that the area (A) of the triangle is half multiplied by base and
perpendicular.
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times x$ $cm^2$.
Now substitute the value of x in this equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 6 = 18$ $cm^2$.
So this is the required area of the right isosceles triangle.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The important step in this question was the area formulation part of an isosceles triangle, as it does not differ from normal triangle as both are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}}$, however for an equilateral triangle in which all the three sides are equal the area is given as $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times {\text{sid}}{{\text{e}}^2}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:

As we know in an isosceles triangle two sides are equal.
Now the given isosceles triangle is a right angle triangle. Therefore its base and perpendicular are equal as shown in figure.
Let its base and perpendicular be x cm.
Now it is given that its hypotenuse is AC = $6\sqrt 2 $ cm.
So apply Pythagoras theorem in right triangle we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} =
{\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2} = {\left( {6\sqrt 2 } \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} = 72$
Now divide by 2 we have,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{72}}{2} = 36 = {6^2}\]
Therefore x = 6 cm.
Now as we know that the area (A) of the triangle is half multiplied by base and
perpendicular.
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times x \times x$ $cm^2$.
Now substitute the value of x in this equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 6 = 18$ $cm^2$.
So this is the required area of the right isosceles triangle.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: The important step in this question was the area formulation part of an isosceles triangle, as it does not differ from normal triangle as both are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{height}}$, however for an equilateral triangle in which all the three sides are equal the area is given as $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times {\text{sid}}{{\text{e}}^2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




