
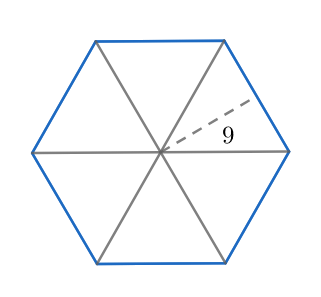
What is the area of a hexagon with an apothem of $9$ ?
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: At first, we divide the hexagon into six equilateral triangles. As we are given the height of one triangle, we can calculate the area of it using two formulae $h=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$ , and $Area=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}$ . Hence by multiplying the area of one triangle by six, we can get the area of the entire hexagon.
Complete step by step answer:
The apothem is the distance between the centre of a polygon and the midpoint of one of its sides. In the given problem, the polygon is a hexagon (six sides). The hexagon has several properties associated with it. One of the properties is that if we join the centre to all the vertices then we get six equilateral triangles, all of the triangles having the same area.
The apothem of a hexagon is basically the height of the equilateral triangle. We have a predefined relation between the side and height of an equilateral triangle, which is
$h=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$ where “h” is the height and “a” is the side of the triangle.
Now putting the value of $h=9$ , we get the value of “a” as,
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\left( 9 \right)=6\sqrt{3}$
As we know the area of an equilateral triangle is,
$Area=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}$, hence putting the value of $a=6\sqrt{3}$ , we get the area as $27\sqrt{3}$ . Now we have a total of $6$ equilateral triangles. Hence the total area of the hexagon is $6\times 27\sqrt{3}=162\sqrt{3}$ .
Note: We should be aware of the less commonly used terms such as apothem. We should draw the diagrams carefully and carry out the various calculations attentively. At last, we should remember the number of triangles with the area of one triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
The apothem is the distance between the centre of a polygon and the midpoint of one of its sides. In the given problem, the polygon is a hexagon (six sides). The hexagon has several properties associated with it. One of the properties is that if we join the centre to all the vertices then we get six equilateral triangles, all of the triangles having the same area.
The apothem of a hexagon is basically the height of the equilateral triangle. We have a predefined relation between the side and height of an equilateral triangle, which is
$h=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a$ where “h” is the height and “a” is the side of the triangle.
Now putting the value of $h=9$ , we get the value of “a” as,
$\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\left( 9 \right)=6\sqrt{3}$
As we know the area of an equilateral triangle is,
$Area=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{a}^{2}}$, hence putting the value of $a=6\sqrt{3}$ , we get the area as $27\sqrt{3}$ . Now we have a total of $6$ equilateral triangles. Hence the total area of the hexagon is $6\times 27\sqrt{3}=162\sqrt{3}$ .

Note: We should be aware of the less commonly used terms such as apothem. We should draw the diagrams carefully and carry out the various calculations attentively. At last, we should remember the number of triangles with the area of one triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




