
How are ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}$ and ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ prepared? Give the structures.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: Xenon is a gas that is used in flash and arc lamps, as well as as a general anaesthetic. The first excimer laser used a xenon dimer molecule as the lasing medium, and the first laser pumps were xenon flash lamps. Xenon is used as a propellant for ion thrusters in satellites and to scan for possible weakly interacting large particles.
Complete answer: The chemical element xenon has the symbol Xe and the atomic number 54. It is a colourless, thick, and odourless noble gas present in trace concentrations in the Earth's atmosphere. Xenon can undergo a few chemical reactions, including the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesised.
In its +6 oxidation state, xenon trioxide is an acidic xenon compound. It's a powerful oxidizer that steadily releases oxygen from water, which is accelerated by exposure to sunlight. When it comes into contact with organic products, it becomes dangerously explosive. It emits xenon and oxygen gas as it detonates.
Fluorides of xenon always react with water vigorously to form ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
$\mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon hexafluoride }}} + \mathop {3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon trioxide }}} + 6{\text{HF}}$
$\mathop {3{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon tetrafluoride }}} + \mathop {6{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {2{\text{Xe}}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon }}} + \mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon trioxide }}} + 12{\text{HF}} + 1\dfrac{1}{2}{{\text{O}}_2}$

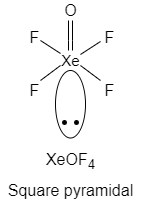
Sometimes Partial hydrolysis of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}$ yields ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_4}$
The chemical compound xenon oxytetrafluoride is an inorganic compound. It's a colourless, solid liquid with a melting point of $-46.2^oC$ that's made by partially hydrolyzing \[Xe{F_6}\].
$\mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon hexafluoride }}} + \mathop {{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {{\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_4}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon oxytetrafluoride }}} + \mathop {2{\text{HF}}}\limits_{{\text{ Hydrogen fluoride }}} $
Note:
Seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes make up naturally occurring xenon. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes decay radioactively, and xenon isotope ratios are a useful instrument for researching the Solar System's early history. The most important (and unwanted) neutron absorber in nuclear reactors is radioactive xenon-135, which is formed by beta decay from iodine-135 (a result of nuclear fission).
Complete answer: The chemical element xenon has the symbol Xe and the atomic number 54. It is a colourless, thick, and odourless noble gas present in trace concentrations in the Earth's atmosphere. Xenon can undergo a few chemical reactions, including the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesised.
In its +6 oxidation state, xenon trioxide is an acidic xenon compound. It's a powerful oxidizer that steadily releases oxygen from water, which is accelerated by exposure to sunlight. When it comes into contact with organic products, it becomes dangerously explosive. It emits xenon and oxygen gas as it detonates.
Fluorides of xenon always react with water vigorously to form ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
$\mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon hexafluoride }}} + \mathop {3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon trioxide }}} + 6{\text{HF}}$
$\mathop {3{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_4}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon tetrafluoride }}} + \mathop {6{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {2{\text{Xe}}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon }}} + \mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_3}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon trioxide }}} + 12{\text{HF}} + 1\dfrac{1}{2}{{\text{O}}_2}$

Sometimes Partial hydrolysis of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}$ yields ${\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_4}$
The chemical compound xenon oxytetrafluoride is an inorganic compound. It's a colourless, solid liquid with a melting point of $-46.2^oC$ that's made by partially hydrolyzing \[Xe{F_6}\].
$\mathop {{\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_6}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon hexafluoride }}} + \mathop {{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{ Water }}} \to \mathop {{\text{XeO}}{{\text{F}}_4}}\limits_{{\text{ Xenon oxytetrafluoride }}} + \mathop {2{\text{HF}}}\limits_{{\text{ Hydrogen fluoride }}} $

Note:
Seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes make up naturally occurring xenon. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes decay radioactively, and xenon isotope ratios are a useful instrument for researching the Solar System's early history. The most important (and unwanted) neutron absorber in nuclear reactors is radioactive xenon-135, which is formed by beta decay from iodine-135 (a result of nuclear fission).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




