
Why are there more stomata present on the underside of the leaf?
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: The microscopic apertures found on the epidermis of leaves are known as stomata. Stomata can be seen with a light microscope. Stomata can be seen on stems and other parts of plants in some species. Stomata are essential for gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. They regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the vents.
Complete answer:
Stomata are made up of tiny pores termed stoma that are encircled by a pair of guard cells. Stomata open and close in response to guard cell turgidity. The pore is surrounded by a strong and flexible cell wall. This is a strategy for preventing excessive water loss. Because dicot leaves are held horizontally, the upper epidermis receives direct light. To allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through, the stomata must be open during daylight hours. Water vapour leaks into the atmosphere while they are open (transpiration). If the stomata are present on the plant's lower surface, they will be less exposed to the sun and more protected from the breeze. Transpiration is the loss of water through stomata, hence the lower surface has more stomata to prevent excessive water loss.
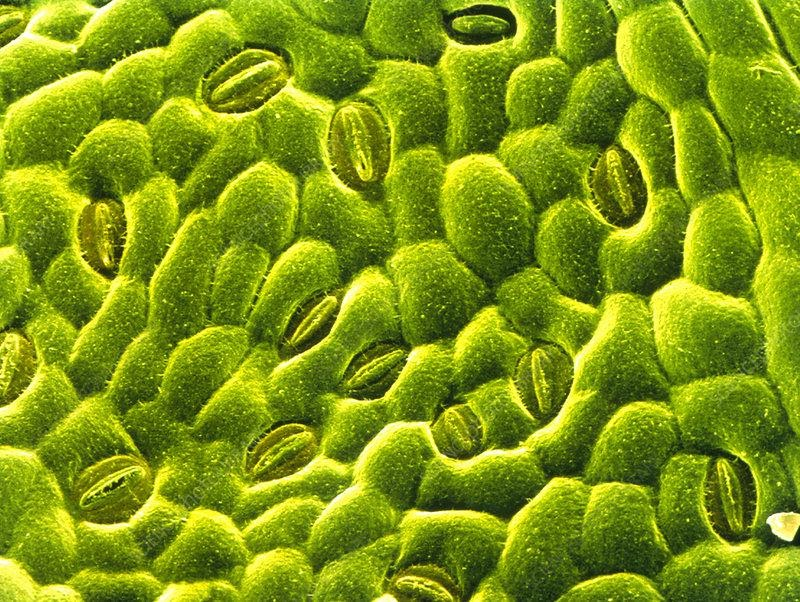
STOMATA ON UNDERSIDE OF THE LEAF
Note:
The following are the primary roles of stomata:
Stomatal opening and closure help with gaseous exchange between the plant and the environment.
It aids in the elimination of surplus water in the form of water vapour through transpiration.
Water does not escape through pores while the stomata are closed at night.
By opening and shutting in response to the weather, it maintains the moisture balance.
During photosynthesis, stomata aid in the uptake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen.
Complete answer:
Stomata are made up of tiny pores termed stoma that are encircled by a pair of guard cells. Stomata open and close in response to guard cell turgidity. The pore is surrounded by a strong and flexible cell wall. This is a strategy for preventing excessive water loss. Because dicot leaves are held horizontally, the upper epidermis receives direct light. To allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through, the stomata must be open during daylight hours. Water vapour leaks into the atmosphere while they are open (transpiration). If the stomata are present on the plant's lower surface, they will be less exposed to the sun and more protected from the breeze. Transpiration is the loss of water through stomata, hence the lower surface has more stomata to prevent excessive water loss.

STOMATA ON UNDERSIDE OF THE LEAF
Note:
The following are the primary roles of stomata:
Stomatal opening and closure help with gaseous exchange between the plant and the environment.
It aids in the elimination of surplus water in the form of water vapour through transpiration.
Water does not escape through pores while the stomata are closed at night.
By opening and shutting in response to the weather, it maintains the moisture balance.
During photosynthesis, stomata aid in the uptake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




