
What are the two requirements for oscillation?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint:Let us first know about oscillators. An oscillator is an electrical device that generates the voltage of an AC signal. From very low frequencies to very high frequencies, oscillators generate sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal waveforms. Most modern broadcast band AM superheterodyne have a local oscillator that covers a frequency range of \[1000{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}2100{\text{ }}KHz\](approximately).
Complete step-by-step solution:
An oscillator circuit is just an amplifier that provides itself with an input signal (through feedback). It is a nonrotating device that produces alternating current, with the output frequency defined by the device's properties. An Oscillator's primary function is to generate a waveform with a consistent peak amplitude and precise frequency and to keep it within predefined amplitude and frequency constraints.
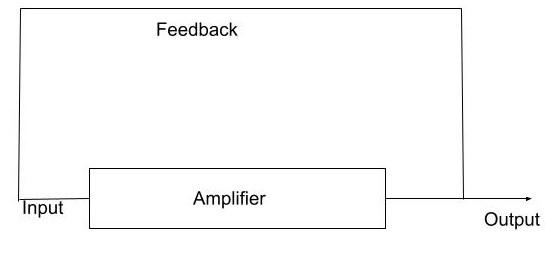
Two Oscillation Requirements:
1. To produce the signal with the required gain, the oscillator requires amplification.
2. The oscillator needs enough regeneration feedback to keep oscillations going.
The following two types of electronic oscillators can be generally classified.
The oscillators that produce a sine wave output are known as sinusoidal or harmonic oscillators. The output frequency of such oscillators can range from \[20\] Hz to GHz.
Non-sinusoidal or relaxation oscillators are oscillators that produce a square, rectangular, or saw tooth waveform as an output. Oscillators of this type can provide output at frequencies ranging from \[0{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}20\]Mhz.
Note:An oscillator's frequency stability is a measure of its ability to keep a consistent frequency over a lengthy period of time. However, it has been discovered that if an oscillator is tuned to a specific frequency, it does not retain that frequency for a long time.
Complete step-by-step solution:
An oscillator circuit is just an amplifier that provides itself with an input signal (through feedback). It is a nonrotating device that produces alternating current, with the output frequency defined by the device's properties. An Oscillator's primary function is to generate a waveform with a consistent peak amplitude and precise frequency and to keep it within predefined amplitude and frequency constraints.

Two Oscillation Requirements:
1. To produce the signal with the required gain, the oscillator requires amplification.
2. The oscillator needs enough regeneration feedback to keep oscillations going.
The following two types of electronic oscillators can be generally classified.
The oscillators that produce a sine wave output are known as sinusoidal or harmonic oscillators. The output frequency of such oscillators can range from \[20\] Hz to GHz.
Non-sinusoidal or relaxation oscillators are oscillators that produce a square, rectangular, or saw tooth waveform as an output. Oscillators of this type can provide output at frequencies ranging from \[0{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}20\]Mhz.
Note:An oscillator's frequency stability is a measure of its ability to keep a consistent frequency over a lengthy period of time. However, it has been discovered that if an oscillator is tuned to a specific frequency, it does not retain that frequency for a long time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




