
What are the three principles of cell theory?
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: All living things are made up of cells, which are the structural, functional, and biological components. A cell has the capability of self-replication. As a result, they've earned the moniker "life's building blocks". Each cell contains a fluid called cytoplasm, which is enclosed by a membrane. Biomolecules found in the cytoplasm include proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Cell organelles suspended in the cytoplasm are also present. Cells are comparable to factories in that they have various workers and departments working toward a shared goal. Distinct types of cells have different purposes. There are two types of cells based on their cellular structure: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Complete answer:
Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory, which was later modified by Rudolf Virchow. The following are the three principles of cell theory:
1. Every living thing is made up of one or more cells.
2. Living organisms are made up of cells, which are the basic structural and functional units.
3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Cells make up all living species, whether bacteria or large multicellular animals. Cells have the same basic chemical composition, albeit the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells, differs.
A single cell in prokaryotes, such as bacteria, and unicellular eukaryotes, such as amoebae, performs all of the processes required for life. There is division of labour in multicellular organisms, and cells are specialised to perform specific functions.
Complex multicellular organisms emerge from a single-cell zygote. At the moment of cell division, cells carry all of the genetic information, which is passed on to the progeny.
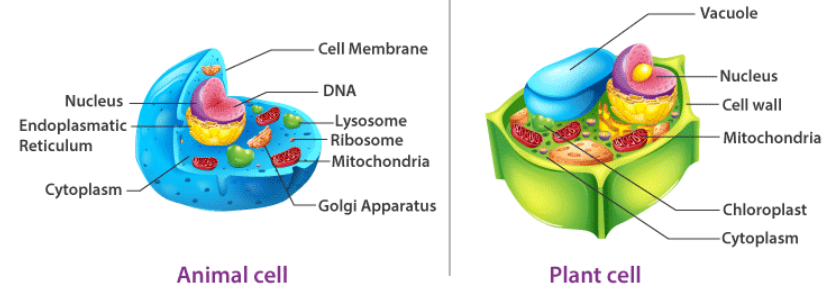
STRUCTURE AND COMPONENTS OF CELL
Note:
Characteristics of cells:
Cells sustain and structure the body of an organism.
The interior of the cell is separated into various organelles, each with its own membrane.
The nucleus (major organelle) stores genetic data required for cell reproduction and growth.
Each cell has a single nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria, a double membrane-bound organelle, is in charge of the majority of energy exchanges necessary for cell survival.
Lysosomes break down waste products in the cell.
Complete answer:
Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory, which was later modified by Rudolf Virchow. The following are the three principles of cell theory:
1. Every living thing is made up of one or more cells.
2. Living organisms are made up of cells, which are the basic structural and functional units.
3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Cells make up all living species, whether bacteria or large multicellular animals. Cells have the same basic chemical composition, albeit the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells, differs.
A single cell in prokaryotes, such as bacteria, and unicellular eukaryotes, such as amoebae, performs all of the processes required for life. There is division of labour in multicellular organisms, and cells are specialised to perform specific functions.
Complex multicellular organisms emerge from a single-cell zygote. At the moment of cell division, cells carry all of the genetic information, which is passed on to the progeny.

STRUCTURE AND COMPONENTS OF CELL
Note:
Characteristics of cells:
Cells sustain and structure the body of an organism.
The interior of the cell is separated into various organelles, each with its own membrane.
The nucleus (major organelle) stores genetic data required for cell reproduction and growth.
Each cell has a single nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria, a double membrane-bound organelle, is in charge of the majority of energy exchanges necessary for cell survival.
Lysosomes break down waste products in the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




