
What are the structure and function of alveoli?
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: The alveoli are the functional unit of lungs. The air inhaled through the nostrils passes through the trachea and enter the lungs through bronchi. The bronchi further divide into bronchioles and finally end up in an air sac called alveoli.
Complete answer:
Alveoli are tiny air sacs present within the lungs which appear as a bunch of grapes. These also are referred to as pulmonary alveoli. They mainly promote the exchange of gases. Let us discuss the structure and function of alveoli in detail.
Alveoli structure: The pulmonary alveolus may be a sac roughly 0.2 to 0.5 mm in diameter. These alveoli are located at the ends of air passageways within the lungs. Sometimes, people compare alveoli structures to the looks of a raspberry or a “bunch of grapes.” within the average adult lung, there's a mean of 480 million alveoli.
Things are often said about the alveolar shape and structure:
- Largely polyhedral shape
- Open at one end, sort of a cup
- The walls of the alveoli are composed of the pulmonary capillary sheet
- Alveolar surfaces are covered during a thin (200 nm) layer of surfactant which acts because the interface with the gas
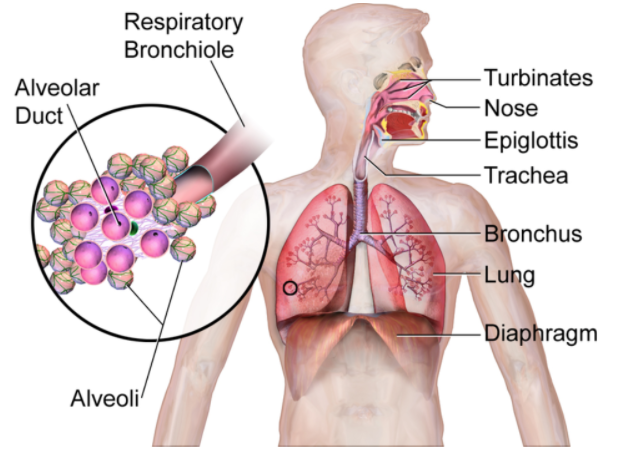
Alveoli function: Alveoli are the endpoint of the systema respiratorium which starts once we inhale air into the mouth or nose. The oxygen-rich air travels down the trachea then into one among the 2 lungs via the proper or left bronchus. Carbon dioxide molecules, a by-product of respiration, are diffused back to the alveolus where they're expelled out of the body through the nose or mouth. During inhalation, alveoli expand because the negative pressure within the chest is made by the contraction of the diaphragm. During exhalation, the alveoli recoil (spring back) because the diaphragm relaxes.
Note: The alveoli allow the diffusion of gases between the lungs and the blood by exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out. Oxygen breathed in from the air passes through the alveoli and into the blood and travels to the tissues throughout the body.
Complete answer:
Alveoli are tiny air sacs present within the lungs which appear as a bunch of grapes. These also are referred to as pulmonary alveoli. They mainly promote the exchange of gases. Let us discuss the structure and function of alveoli in detail.
Alveoli structure: The pulmonary alveolus may be a sac roughly 0.2 to 0.5 mm in diameter. These alveoli are located at the ends of air passageways within the lungs. Sometimes, people compare alveoli structures to the looks of a raspberry or a “bunch of grapes.” within the average adult lung, there's a mean of 480 million alveoli.
Things are often said about the alveolar shape and structure:
- Largely polyhedral shape
- Open at one end, sort of a cup
- The walls of the alveoli are composed of the pulmonary capillary sheet
- Alveolar surfaces are covered during a thin (200 nm) layer of surfactant which acts because the interface with the gas

Alveoli function: Alveoli are the endpoint of the systema respiratorium which starts once we inhale air into the mouth or nose. The oxygen-rich air travels down the trachea then into one among the 2 lungs via the proper or left bronchus. Carbon dioxide molecules, a by-product of respiration, are diffused back to the alveolus where they're expelled out of the body through the nose or mouth. During inhalation, alveoli expand because the negative pressure within the chest is made by the contraction of the diaphragm. During exhalation, the alveoli recoil (spring back) because the diaphragm relaxes.
Note: The alveoli allow the diffusion of gases between the lungs and the blood by exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out. Oxygen breathed in from the air passes through the alveoli and into the blood and travels to the tissues throughout the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




