
What are the six trigonometric functions of the right triangle?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: In a right angled triangle, For finding the trigonometric ratios we use the pythagorean theorem and side ratios which are named as trigonometric ratios.
Pythagoras theorem: Sum of the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
Sides: In a right angle triangle we have three types of sides viz., hypotenuse side, base side and perpendicular sides.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this problem, we need to define the six trigonometric functions of the right triangle.
Let us consider that the hypotenuse side be
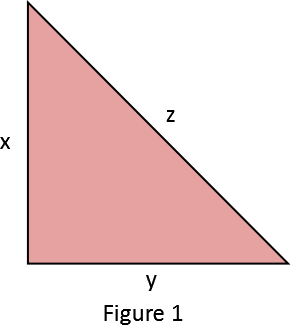
The assumed right angled triangle is show above in the Figure 1
The formula for six trigonometric ratios are as follows:
The formula for sine function is
\[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{z}\]
The formula for cosine function is
\[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{z}\]
The formula for tangent function is
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{\text{perpendicular side}}{\text{base side}}$
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\tan \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
The formula for cosecant function is
\[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{z}{x}\]
The formula for secant function is
$\sec \theta = \dfrac{\text{hypotenuse side}}{\text{base side}}$
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\sec \,\theta = \dfrac{z}{y}\]
The formula for cotangent function is
\[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{x}\]
Therefore, the six trigonometric functions are \[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{z}\], \[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{z}\], \[\tan \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{y}\], \[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{z}{x}\], \[\sec \,\theta = \dfrac{z}{y}\]and \[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{x}\]respectively.
Note: The ratio between the perpendicular and the hypotenuse sides is called the sine function (written as \[\sin \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called as the cosecant function (written as \[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta \]).
The ratio between the base and the hypotenuse sides is called the cosine function (written as \[\cos \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called the secant function (written as \[\sec \,\theta \]).
The ratio between the perpendicular and the base sides is called the tangent function (written as \[\tan \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called as the cotangent function (written as \[\cot \,\theta \]).
Pythagoras theorem: Sum of the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
Sides: In a right angle triangle we have three types of sides viz., hypotenuse side, base side and perpendicular sides.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In this problem, we need to define the six trigonometric functions of the right triangle.
Let us consider that the hypotenuse side be
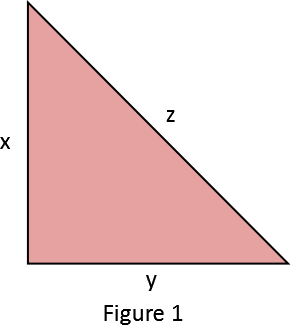
The assumed right angled triangle is show above in the Figure 1
The formula for six trigonometric ratios are as follows:
The formula for sine function is
\[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{z}\]
The formula for cosine function is
\[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{z}\]
The formula for tangent function is
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{\text{perpendicular side}}{\text{base side}}$
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\tan \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
The formula for cosecant function is
\[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{z}{x}\]
The formula for secant function is
$\sec \theta = \dfrac{\text{hypotenuse side}}{\text{base side}}$
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\sec \,\theta = \dfrac{z}{y}\]
The formula for cotangent function is
\[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{perpendicular}}\,{\text{side}}}}\]
From the Figure 1 we get,
\[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{x}\]
Therefore, the six trigonometric functions are \[\sin \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{z}\], \[\cos \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{z}\], \[\tan \,\theta = \dfrac{x}{y}\], \[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta = \dfrac{z}{x}\], \[\sec \,\theta = \dfrac{z}{y}\]and \[\cot \,\theta = \dfrac{y}{x}\]respectively.
Note: The ratio between the perpendicular and the hypotenuse sides is called the sine function (written as \[\sin \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called as the cosecant function (written as \[\cos {\text{ec}}\,\theta \]).
The ratio between the base and the hypotenuse sides is called the cosine function (written as \[\cos \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called the secant function (written as \[\sec \,\theta \]).
The ratio between the perpendicular and the base sides is called the tangent function (written as \[\tan \,\theta \]) and the reciprocal of this ratio is called as the cotangent function (written as \[\cot \,\theta \]).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




