
What are the sex-linked diseases? Write down the names of two sex-linked diseases.
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: These are recessive disorders associated with one of the allosomes. There are recessive and dominant diseases. X-linked recessive diseases are more common among males than females.
Complete answer:
Sex-linked diseases: These are traits that are found on either one among the chromosomes that determine sex, or the sex chromosomes. And in humans, this is often the X or the Y chromosomes. then a number of the more familiar sex-linked traits are haemophilia, red-green colour blindness, congenital night blindness, some high blood pressure genes, Duchenne dystrophy, and also Fragile X syndrome. So what's also very interesting is that you simply can imagine that for people who are XY or males, having these different mutations on the genes, on the X chromosome, is especially problematic, because unlike females, there aren't two X chromosomes that offer you the potential of carrying a traditional gene on the X chromosome. Which is why in many cases you will see that males are more often afflicted with these sex-linked disorders.
Examples: Haemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy.
Additional Information:
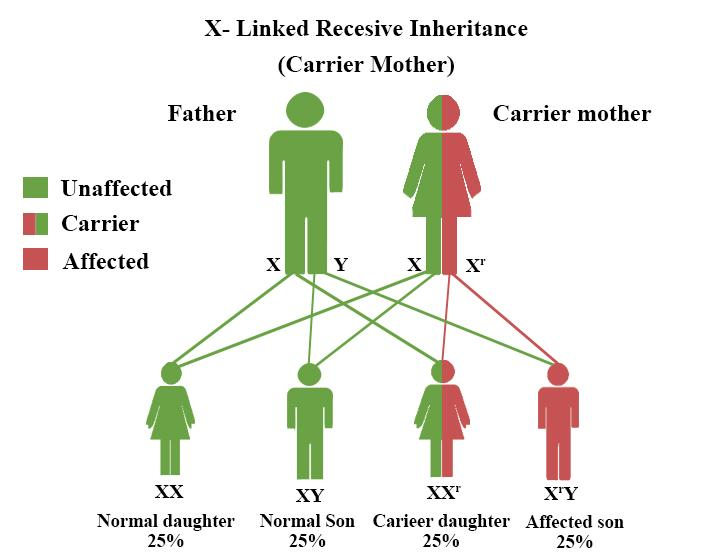
Note: -Sex-linked diseases can be dominant and recessive.
-Most commonly males are observed to get affected by this type of disease.
-X and Y are sex chromosomes. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease, although the matching gene from the opposite parent is normal. The abnormal gene dominates. Whereas in the case of recessive, both the genes must be abnormal.
Complete answer:
Sex-linked diseases: These are traits that are found on either one among the chromosomes that determine sex, or the sex chromosomes. And in humans, this is often the X or the Y chromosomes. then a number of the more familiar sex-linked traits are haemophilia, red-green colour blindness, congenital night blindness, some high blood pressure genes, Duchenne dystrophy, and also Fragile X syndrome. So what's also very interesting is that you simply can imagine that for people who are XY or males, having these different mutations on the genes, on the X chromosome, is especially problematic, because unlike females, there aren't two X chromosomes that offer you the potential of carrying a traditional gene on the X chromosome. Which is why in many cases you will see that males are more often afflicted with these sex-linked disorders.
Examples: Haemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy.
Additional Information:
| Autosomal inheritance | X-linked Inheritance |
| It is the pattern of inheritance in which the transmission of traits depends on the genes in the autosome. | It is the pattern of inheritance in which the transmission of traits depends on the genes in the sex chromosomes. |
| Describes the inheritance pattern in the genes in the autosome. | Describes the inheritance pattern in the genes in one of the sex chromosome. |
| Exhibits Mendelian inheritance. | Exhibits criss-cross inheritance. |
| The autosomal trait is controlled by both the alleles of a gene. | Alleles in the X-chromosomes are often involved in the determination of the X-linked trait. |
| It equally affects both the sexes. | It affects one of the sex, often male individuals are observed. |
| Autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive are the types of this. | X-linked dominant and X-linked recessive are the two types. |
| Male to male transmission is observed. | Male to male transmission is not observed. |

Note: -Sex-linked diseases can be dominant and recessive.
-Most commonly males are observed to get affected by this type of disease.
-X and Y are sex chromosomes. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent causes disease, although the matching gene from the opposite parent is normal. The abnormal gene dominates. Whereas in the case of recessive, both the genes must be abnormal.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




