
What are the products of a single-displacement reaction when magnesium metal $ \left( {Mg} \right) $ reacts with copper sulphate $ \left( {CuS{O_4}} \right) $ ?
Answer
498.9k+ views
Hint: When a metal which is more reactive replaces the position of another metal which is combined with another atom or molecule is known as single-displacement reaction alternatively known as single-replacement reaction.
Complete answer:
As we know that in the reactivity series of metals, metals are arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity which means metals which are more reactive are placed below the series whereas metals which are less reactive are placed above the series. This series comes forward after performing displacement reactions between metals and their salt solution.
The reactivity series is:
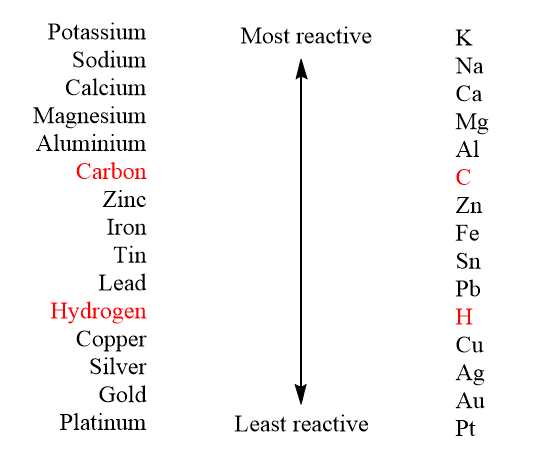
As we can see from the table, the magnesium element is placed higher in the series than copper. So by this we can conclude that magnesium is more reactive than copper. Thus when magnesium reacts with copper sulphate, it replaces copper and forms magnesium sulphate. Copper is reduced into copper atoms which precipitate down whereas magnesium is oxidised and goes into the aqueous phase, displacing copper effectively. Magnesium sulphate is mostly a white crystalline solid which is soluble in water but not in ethanol.
The chemical equation of this will be:
$ Mg + CuS{O_4} \to Cu + MgS{O_4} $
Thus the product of single displacement reaction between magnesium and copper sulphate are copper metal as precipitate and magnesium sulphate.
Note:
The single-displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which one atom replaces another atom. It can be representing as:
$ A + BC \to AC + B $
Where $ A $ and $ B $ both are different metals, $ C $ is the anion.
This reaction occurs more frequently if $ A $ is more reactive than $ B $ , so give a more stable product.
Complete answer:
As we know that in the reactivity series of metals, metals are arranged in the decreasing order of reactivity which means metals which are more reactive are placed below the series whereas metals which are less reactive are placed above the series. This series comes forward after performing displacement reactions between metals and their salt solution.
The reactivity series is:

As we can see from the table, the magnesium element is placed higher in the series than copper. So by this we can conclude that magnesium is more reactive than copper. Thus when magnesium reacts with copper sulphate, it replaces copper and forms magnesium sulphate. Copper is reduced into copper atoms which precipitate down whereas magnesium is oxidised and goes into the aqueous phase, displacing copper effectively. Magnesium sulphate is mostly a white crystalline solid which is soluble in water but not in ethanol.
The chemical equation of this will be:
$ Mg + CuS{O_4} \to Cu + MgS{O_4} $
Thus the product of single displacement reaction between magnesium and copper sulphate are copper metal as precipitate and magnesium sulphate.
Note:
The single-displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which one atom replaces another atom. It can be representing as:
$ A + BC \to AC + B $
Where $ A $ and $ B $ both are different metals, $ C $ is the anion.
This reaction occurs more frequently if $ A $ is more reactive than $ B $ , so give a more stable product.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




