
What are the hydrolysis products of glyceryl oleate ${{({{C}_{17}}{{H}_{32}}COOH)}_{3}}{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{5}}$ during the preparation of soap?
(A)- ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{32}}COONa+{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{5}}OH$
(B)- ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{35}}COOH+C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$
(C)- ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{32}}COOH+C{{H}_{2}}OH-CHOH-C{{H}_{2}}OH$
(D)- ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{33}}COONa+C{{H}_{2}}OH-CHOH-C{{H}_{2}}OH$
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Fats and oils are the triesters of glycerol, thus they are known as triacylglycerol or triglycerides. Soap is prepared by the hydrolysis of triglycerides with alkalies, and this process of preparation of soap by alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils is called saponification.
Complete answer:
Glyceryl oleate is the triester of glycerol and oleic acid. The structure of glyceryl oleate is shown below:
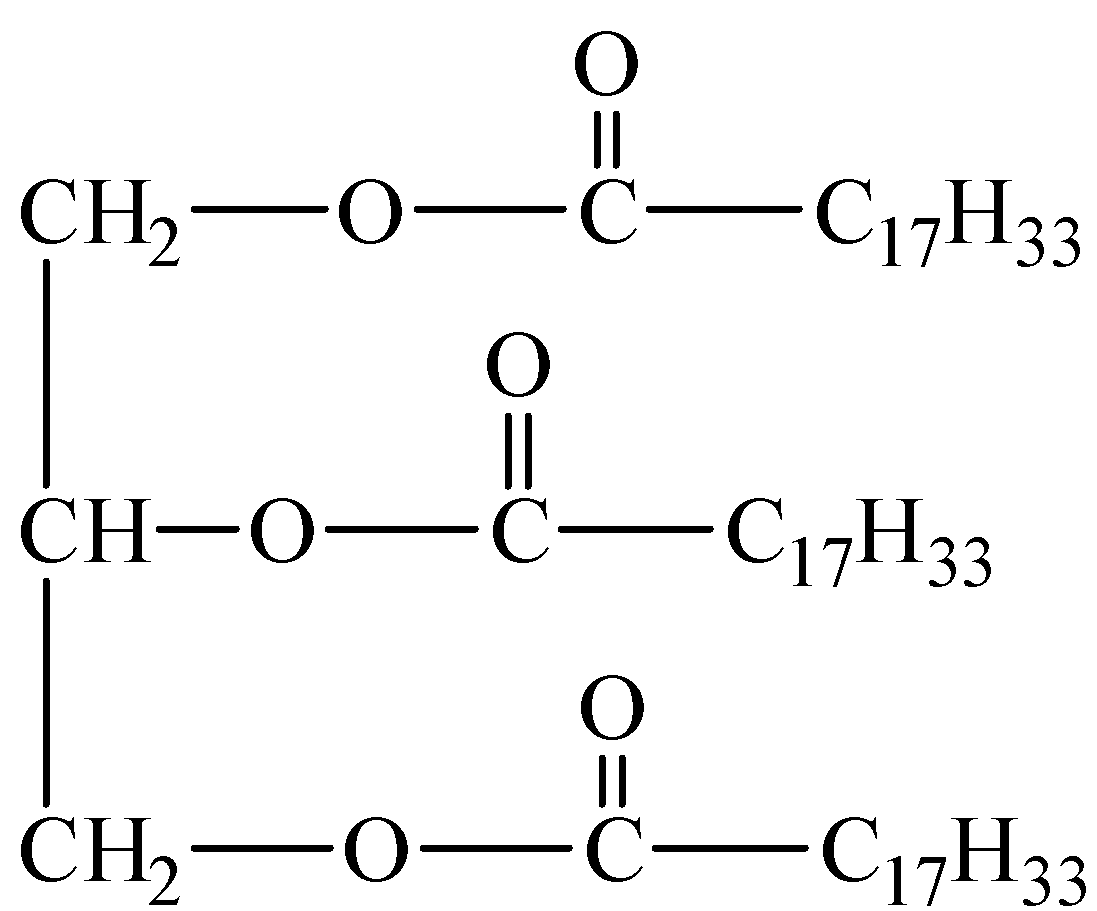
Hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate with alkali such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) results in the formation of sodium salts of oleic acid and glycerol.
Since the sodium salts of oleic acid are used as soap, the alkaline hydrolysis of triglycerides like glyceryl oleate is called saponification. The reaction showing the hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate during the preparation of soap is given below:
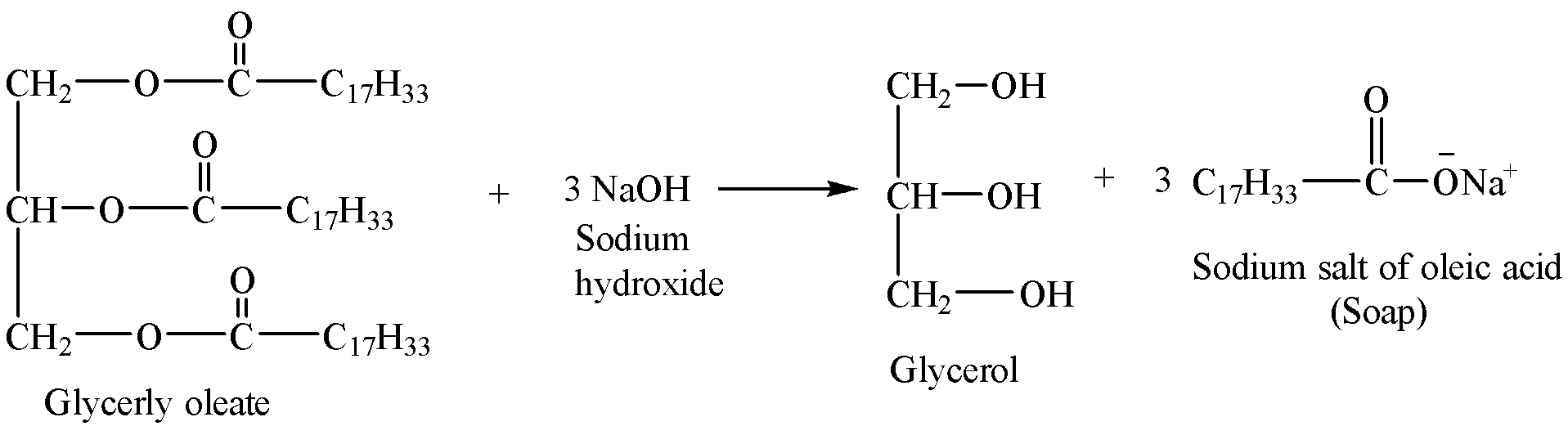
Therefore, the hydrolysis products of glyceryl oleate ${{({{C}_{17}}{{H}_{32}}COOH)}_{3}}{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{5}}$ during the preparation of soap are sodium oleate ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{33}}COONa$ and glycerol $C{{H}_{2}}OH-CHOH-C{{H}_{2}}OH$.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
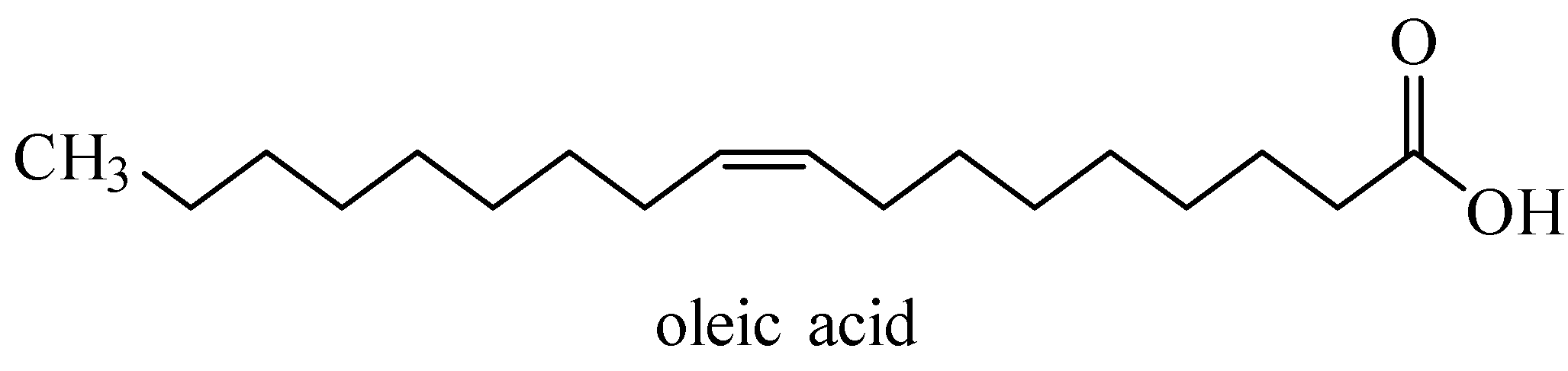
Additional information: Oleic acid (${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{33}}COOH$) is an unsaturated fatty acid and contains one double bond at ${{C}_{9}}$ in cis-orientation.
The term saponification value is commonly used while studying the chemistry of glycerides and soaps. It is the amount of base required to completely saponify one gram of fat or oil. This value tells us about the adulteration of a fat or oil by other fat or oil or other impurities.
Note:
Hydrolysis of fats and oils can also be carried out using mineral acids or water (superheated steam). Note that hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate by steam or acids gives fatty acid, i.e. oleic acid and glycerol whereas hydrolysis by alkaline solution gives salts of oleic acid, which are used as soap, and glycerol.
Complete answer:
Glyceryl oleate is the triester of glycerol and oleic acid. The structure of glyceryl oleate is shown below:

Hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate with alkali such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) results in the formation of sodium salts of oleic acid and glycerol.
Since the sodium salts of oleic acid are used as soap, the alkaline hydrolysis of triglycerides like glyceryl oleate is called saponification. The reaction showing the hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate during the preparation of soap is given below:

Therefore, the hydrolysis products of glyceryl oleate ${{({{C}_{17}}{{H}_{32}}COOH)}_{3}}{{C}_{3}}{{H}_{5}}$ during the preparation of soap are sodium oleate ${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{33}}COONa$ and glycerol $C{{H}_{2}}OH-CHOH-C{{H}_{2}}OH$.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Additional information: Oleic acid (${{C}_{17}}{{H}_{33}}COOH$) is an unsaturated fatty acid and contains one double bond at ${{C}_{9}}$ in cis-orientation.

The term saponification value is commonly used while studying the chemistry of glycerides and soaps. It is the amount of base required to completely saponify one gram of fat or oil. This value tells us about the adulteration of a fat or oil by other fat or oil or other impurities.
Note:
Hydrolysis of fats and oils can also be carried out using mineral acids or water (superheated steam). Note that hydrolysis of glyceryl oleate by steam or acids gives fatty acid, i.e. oleic acid and glycerol whereas hydrolysis by alkaline solution gives salts of oleic acid, which are used as soap, and glycerol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




