
What are the functions of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The brain is divided into the cerebrum, the midbrain, the pons, the medulla, and the cerebellum. The brain stem acts as a relay centre connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It performs many of the body’s automatic functions.
Complete step by step answer:
- The cerebrum serves to control and coordinate movement, temperature, touch, vision, hearing, judgment, reasoning, problem- solving abilities, emotions, and learning.
- The medulla oblongata’s function includes regulating several basic functions of the autonomic nervous system, including respiration, cardiac function, vasodilation, and reflexes like vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.
- The function of the cerebellum is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and also to maintain posture, balance, and equilibrium.
The functions of other parts of the brain are:
- The midbrain serves as the control centre of motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
- The pons functions are to relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with dealing with voluntary and involuntary movements such as sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
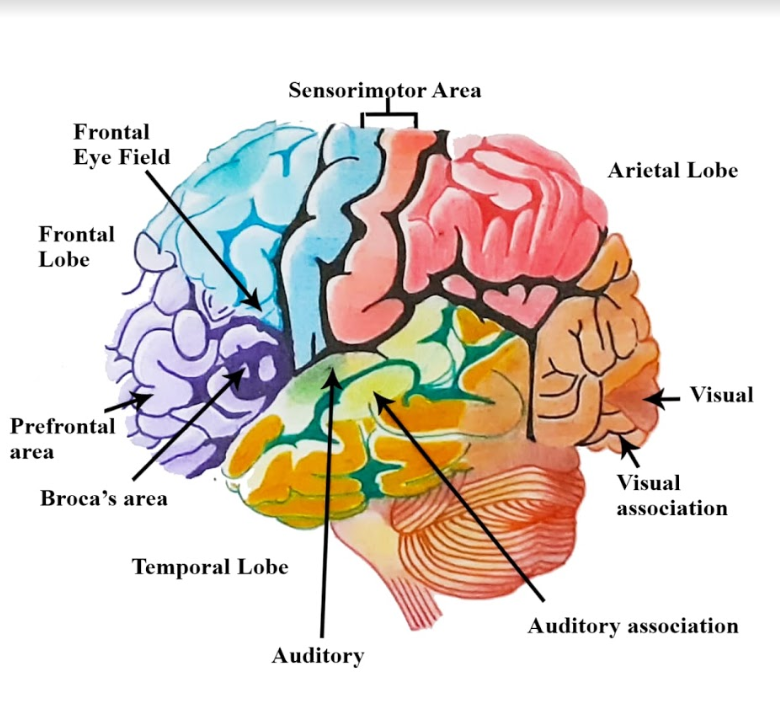
Notes: The nervous system consists of two main parts: The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that arise from the spinal cord and innervates all parts of the body. Each side of the brain comprises four lobes. The frontal lobe is significant in cognitive functions and control of voluntary movements of the body. The parietal lobe deals with the information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement, and the occipital lobe is principally responsible for the vision. The temporal lobe handles the functions related to memories, combining them with sensations of taste, sound, sight, and touch.
Complete step by step answer:
- The cerebrum serves to control and coordinate movement, temperature, touch, vision, hearing, judgment, reasoning, problem- solving abilities, emotions, and learning.
- The medulla oblongata’s function includes regulating several basic functions of the autonomic nervous system, including respiration, cardiac function, vasodilation, and reflexes like vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and swallowing.

- The function of the cerebellum is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and also to maintain posture, balance, and equilibrium.
The functions of other parts of the brain are:
- The midbrain serves as the control centre of motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
- The pons functions are to relay signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum, along with dealing with voluntary and involuntary movements such as sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, and posture.
Notes: The nervous system consists of two main parts: The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that arise from the spinal cord and innervates all parts of the body. Each side of the brain comprises four lobes. The frontal lobe is significant in cognitive functions and control of voluntary movements of the body. The parietal lobe deals with the information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement, and the occipital lobe is principally responsible for the vision. The temporal lobe handles the functions related to memories, combining them with sensations of taste, sound, sight, and touch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




