
What are the formal charges on each atom in sulphite, $ SO_3^{2 - } $ and chlorite, $ ClO_2^ - $ ions?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: Formal charge is a theoretical value assigned to an atom in a molecule which reflects the equal sharing of electrons in a chemical bond, neglecting the electronegativity difference between the atoms. Sketch the Lewis diagram for the given ions to find the value of formal charge of each atom.
Complete answer:
The formal charge can be assigned to an atom with the help of following formula:
$ F = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - (i) $
Where, $ F $ is the formal charge on the atom, $ V $ is the number of electrons of atom in its ground state, $ N $ is the number of lone pair of electrons present on the atom and $ B $ is the number of bonding electrons in that atom.
The Lewis structure for sulphite ions is as follows:
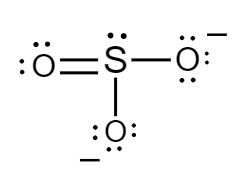
Formal charge for sulphur atom:
Number of electrons of sulphur in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on sulphur atom $ = 2 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 8 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 2 - \dfrac{8}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atoms:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in sulphite ions, the formal charge of sulphur atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atoms is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
The Lewis structure for chlorite ions is as follows:
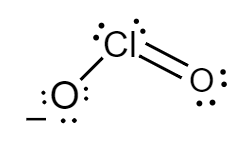
Formal charge for chlorine atom:
Number of electrons of chlorine in its ground state $ = 7 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on chlorine atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 6 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 7 - 4 - \dfrac{6}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in chlorite ions, the formal charge of chlorine atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atom is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
Note:
Lewis structures in which the formal charges are zero for most atoms in the compound, are more preferably considered than the one with non-zero formal charges. Moreover, the negative formal charge should be present on the most electronegative element in the compound.
Complete answer:
The formal charge can be assigned to an atom with the help of following formula:
$ F = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}\,\,\,\,\,\,\, - (i) $
Where, $ F $ is the formal charge on the atom, $ V $ is the number of electrons of atom in its ground state, $ N $ is the number of lone pair of electrons present on the atom and $ B $ is the number of bonding electrons in that atom.
The Lewis structure for sulphite ions is as follows:
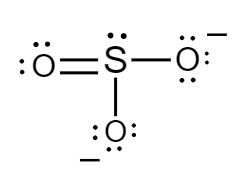
Formal charge for sulphur atom:
Number of electrons of sulphur in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on sulphur atom $ = 2 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 8 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 2 - \dfrac{8}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atoms:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in sulphite ions, the formal charge of sulphur atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atoms is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
The Lewis structure for chlorite ions is as follows:

Formal charge for chlorine atom:
Number of electrons of chlorine in its ground state $ = 7 $
Count of nonbonded electrons present on chlorine atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 6 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 7 - 4 - \dfrac{6}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for doubly bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 4 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 4 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 4 - \dfrac{4}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = 0 $
Formal charge for single bonded oxygen atom:
Number of electrons of oxygen in its ground state $ = 6 $
Count of nonbonded electrons or number of lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom $ = 6 $
Number of bonding electrons $ = 2 $
Substituting values in equation $ (i) $ , formal charge of sulphur atom will be as follows:
$ F = 6 - 6 - \dfrac{2}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - 1 $
Hence, in chlorite ions, the formal charge of chlorine atom, doubly bonded oxygen atom and singly bonded oxygen atom is $ 0,\,0 $ and $ - 1 $ respectively.
Note:
Lewis structures in which the formal charges are zero for most atoms in the compound, are more preferably considered than the one with non-zero formal charges. Moreover, the negative formal charge should be present on the most electronegative element in the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




