
Are the enzymes that catalyze the dark reaction of carbon fixation located inside the thylakoids or outside the thylakoids?
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: The string of biochemical reactions in photosynthesis that do not need light to continue, and eventually create organic molecules from carbon dioxide are called dark reactions. The energy from ATP (formed during the light reactions) drives the dark reactions of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, light-independent reactions are called dark reactions.
Complete answer:
Dark reaction is also known as a carbon-fixing reaction. It is a light-independent procedure in which sugar molecules are created from the carbon dioxide and water molecules. The dark reaction happens in the stroma of the chloroplast, where they consume the products of the light reaction. Plants detain the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by stomata and continue to the Calvin cycle.
This process does not depend straight on the presence of light but is reliant on the products of light reaction i.e., ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions take place through the Calvin cycle. They occur in the stromal matrix of the chloroplast.
The enzymes that catalyze the dark reaction of carbon fixation are present outside the thylakoids. These enzymes are available in the stromal matrix of chloroplasts.
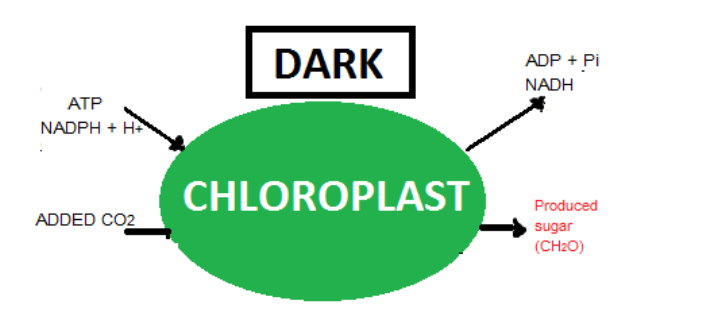
Note: The term dark reactions do not signify the reactions that happen at night or that they want darkness. It means that the reactions can continue regardless of the amount of light available. The term is only used to recognize the dark reactions with the light reactions, which require light. In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH produced during light reaction drive the reaction and exchange six molecules of carbon dioxide into a sugar molecule, i.e. glucose.
Complete answer:
Dark reaction is also known as a carbon-fixing reaction. It is a light-independent procedure in which sugar molecules are created from the carbon dioxide and water molecules. The dark reaction happens in the stroma of the chloroplast, where they consume the products of the light reaction. Plants detain the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by stomata and continue to the Calvin cycle.
This process does not depend straight on the presence of light but is reliant on the products of light reaction i.e., ATP and NADPH. The dark reactions take place through the Calvin cycle. They occur in the stromal matrix of the chloroplast.
The enzymes that catalyze the dark reaction of carbon fixation are present outside the thylakoids. These enzymes are available in the stromal matrix of chloroplasts.

Note: The term dark reactions do not signify the reactions that happen at night or that they want darkness. It means that the reactions can continue regardless of the amount of light available. The term is only used to recognize the dark reactions with the light reactions, which require light. In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH produced during light reaction drive the reaction and exchange six molecules of carbon dioxide into a sugar molecule, i.e. glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




