
what are the E and Z isomers of pent-2-ene?
Answer
532.8k+ views
Hint: Isomers are the compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formula. The E and Z isomerism is the characteristic property of the unsaturated compounds that contain carbon – carbon double bonds as C=C. Z means together while the E prefix means opposite, so the arrangement of atoms is according to E, Z positions.
Complete answer:
Isomers are compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Stereoisomerism is the property of isomers to exist in space. Stereo isomers have different spatial arrangement of the atoms between the same carbon bonds. E and Z isomers describe the stereo aspects of the carbons attached with double bonds.
The E isomer consists of the substituted groups on the opposite sides of the double bond, while in Z isomer, the substituted groups are on the same side of the double bonds.
We have been given pent-2-ene that has a formula$C{{H}_{3}}CH=CHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$, which has a methyl and ethyl as substituted besides the carbon – carbon double bonds.
So, the E isomer where the carbon atoms of the substitutions are on the opposite sides is:
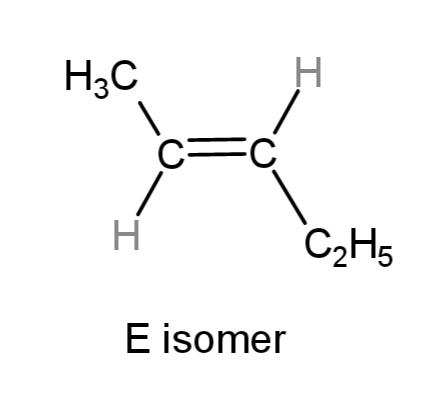
While, the Z isomer where the carbon atoms of the substitutions are on the same sides is:
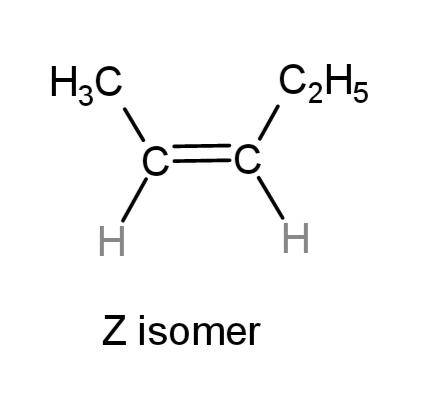
Hence, E and Z isomers are pent-2-ene are as above, with substituted methyl and ethyl groups on opposite and same sides of double bonds respectively.
Note:
Unlike that of the cis and trans geometrical isomerism, E and Z isomerism can have same atoms attached as substituted groups and then also they can be identified as E and Z according to the priority of the atoms substituted. The higher priority atoms are of opposite sides (E) and the lower priority on the same side (Z). Atoms with high atomic numbers are given higher priority.
Complete answer:
Isomers are compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Stereoisomerism is the property of isomers to exist in space. Stereo isomers have different spatial arrangement of the atoms between the same carbon bonds. E and Z isomers describe the stereo aspects of the carbons attached with double bonds.
The E isomer consists of the substituted groups on the opposite sides of the double bond, while in Z isomer, the substituted groups are on the same side of the double bonds.
We have been given pent-2-ene that has a formula$C{{H}_{3}}CH=CHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$, which has a methyl and ethyl as substituted besides the carbon – carbon double bonds.
So, the E isomer where the carbon atoms of the substitutions are on the opposite sides is:

While, the Z isomer where the carbon atoms of the substitutions are on the same sides is:

Hence, E and Z isomers are pent-2-ene are as above, with substituted methyl and ethyl groups on opposite and same sides of double bonds respectively.
Note:
Unlike that of the cis and trans geometrical isomerism, E and Z isomerism can have same atoms attached as substituted groups and then also they can be identified as E and Z according to the priority of the atoms substituted. The higher priority atoms are of opposite sides (E) and the lower priority on the same side (Z). Atoms with high atomic numbers are given higher priority.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




