
Where are the chromosomes found in a cell? State their functions.
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Chromatin material condenses to form thread like structure during cell division called chromosomes.
Complete answer:
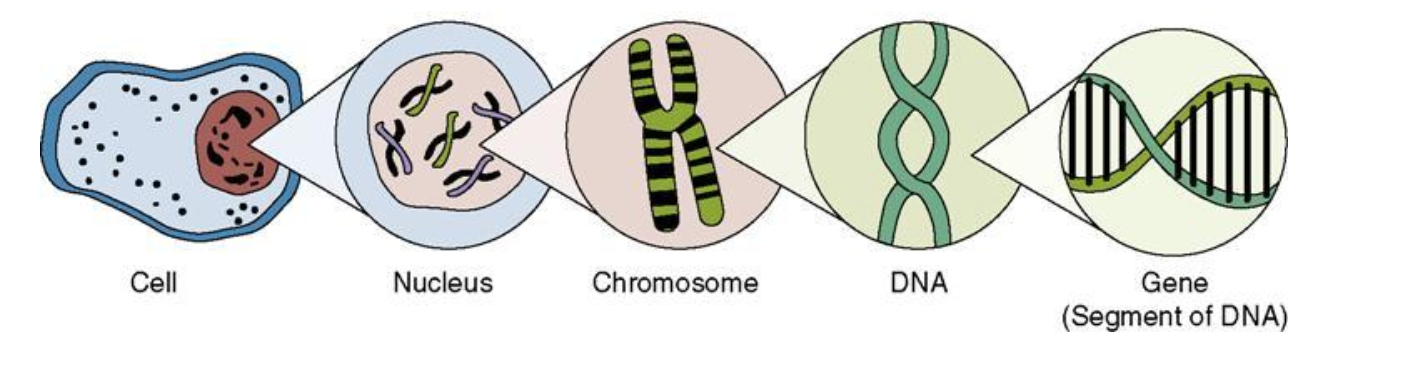
The chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. At different stages of cell division, cells show structured chromosomes in place of the nucleus. Chromatin contains DNA and some basic proteins called histones and some non-histone proteins, and RNA as well. A single human cell has DNA length of 2 metres which is equally distributed among the forty six chromosomes. Every chromosome has a primary constriction called the centromere. On the sides of centromere disc shaped structures called kinetochores are present.
Chromosomes have the following functions -
1. Regulation of cellular proteins.
2. Contains genetic information to control cellular activities.
3. Contains genetic information to develop the basic characteristics of the offspring.
4. Contains information for the production of proteins by the cell.
Additional Information:
The interphase of the nucleus has elaborated nucleoprotein fibres called chromatin and nucleoli. Depending on the position of the kinetochores around the centromere, chromosomes are of four types -
1. Metacentric - Centromere is in the centre forming two equal arms.
2. Sub - metacentric - Centromere is slightly away from the centre leading to formation of one short arm and one long arm.
3. Acrocentric - Centromere is present close to one end, leading to the formation of a very long arm and an extremely short arm.
4. Telocentric - Chromosome has a terminal centrosome.
Notes:
1. Nucleus as an organ was first described by Robert Brown in 1831.
2. Fleming coined the term chromatin for the material of the nucleus stained by basic dyes.
3. The nuclear matrix known as the nucleoplasm contains the nucleolus and chromatin.
Complete answer:
The chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. At different stages of cell division, cells show structured chromosomes in place of the nucleus. Chromatin contains DNA and some basic proteins called histones and some non-histone proteins, and RNA as well. A single human cell has DNA length of 2 metres which is equally distributed among the forty six chromosomes. Every chromosome has a primary constriction called the centromere. On the sides of centromere disc shaped structures called kinetochores are present.
Chromosomes have the following functions -
1. Regulation of cellular proteins.
2. Contains genetic information to control cellular activities.
3. Contains genetic information to develop the basic characteristics of the offspring.
4. Contains information for the production of proteins by the cell.

Additional Information:
The interphase of the nucleus has elaborated nucleoprotein fibres called chromatin and nucleoli. Depending on the position of the kinetochores around the centromere, chromosomes are of four types -
1. Metacentric - Centromere is in the centre forming two equal arms.
2. Sub - metacentric - Centromere is slightly away from the centre leading to formation of one short arm and one long arm.
3. Acrocentric - Centromere is present close to one end, leading to the formation of a very long arm and an extremely short arm.
4. Telocentric - Chromosome has a terminal centrosome.
Notes:
1. Nucleus as an organ was first described by Robert Brown in 1831.
2. Fleming coined the term chromatin for the material of the nucleus stained by basic dyes.
3. The nuclear matrix known as the nucleoplasm contains the nucleolus and chromatin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




