
What are tetrasaccharides? Give their general formula and a few examples.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: Let us analyse the name of the given substance:
- Tetra – Four
- Saccharides – Carbohydrates
This breakdown is a big hint and should point you in the right direction towards solving this question.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first analyse what tetrasaccharides really are before moving on to their general formula.
- A tetrasaccharide is defined as a carbohydrate which, upon hydrolysis, results in the formation of four molecules of similar or different monosaccharides. For instance, stachyose upon hydrolysis gives one molecule each of glucose and fructose and two molecules of galactose. However they are in their respective furanose and pyranose form when involved in tetrasaccharide. Its structure is as follows:
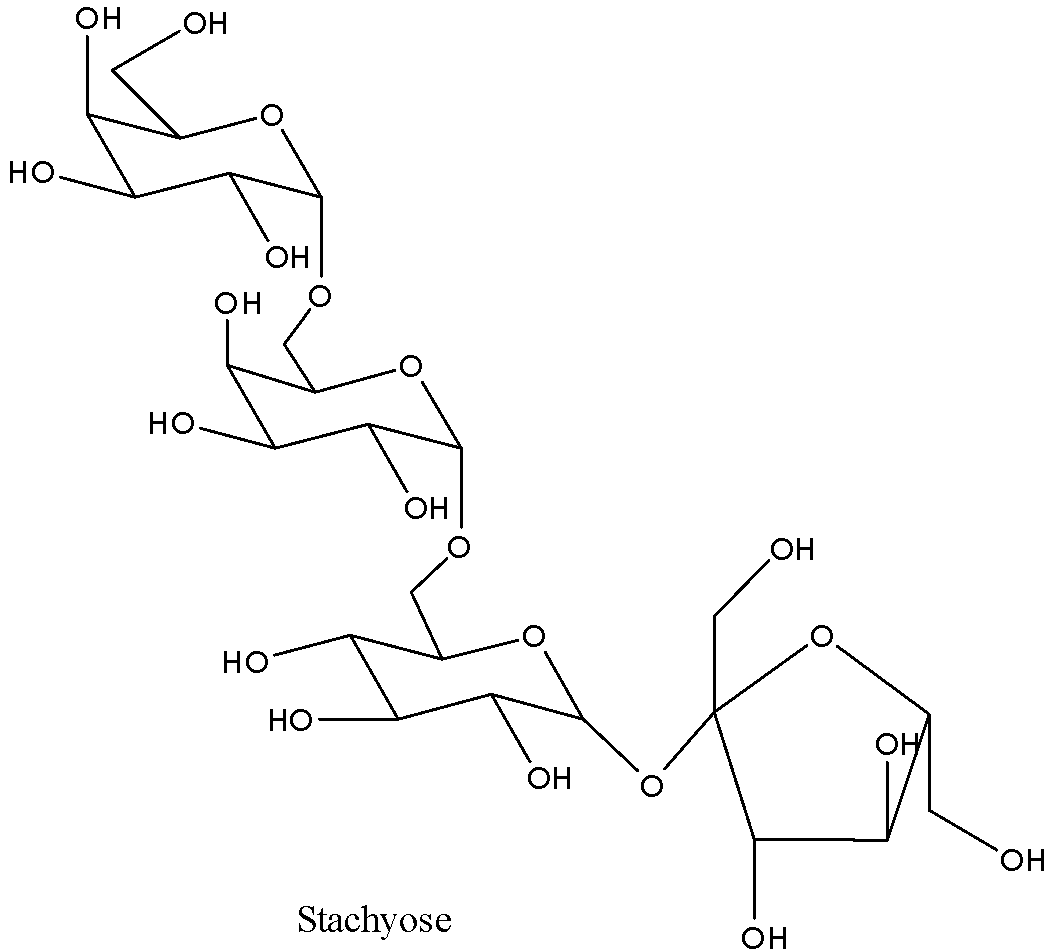
Observe the presence of four different monosaccharide structures present in its overall chemical structure. In its hydrolysis, notice that a water molecule has effectively been added across the glycosidic linkages resulting in the formation of four monosaccharides; glucose, fructose and two molecules of galactose.
\[\text{Tetrasaccharide}\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}4\cdot \text{Monosaccharide}\]
The general formula of a tetrasaccharide is ${{C}_{24}}{{H}_{42}}{{O}_{21}}$ .
Another very important example of a tetrasaccharide is Maltotetraose, which is a kind of Maltodextrin which is a polysaccharide (many carbohydrates joined together in a molecular chain) that is used as a food additive which is easily digestible, being absorbed as rapidly as glucose and may be either moderately sweet or almost flavourless.
- In addition to them, Lychnose, Maltotetrose and Sesame are also examples of tetrasaccharides.
Note: We can say that all tetrasaccharides are oligosaccharides, but we cannot say that all oligosaccharides are tetrasaccharides because oligosaccharides involves carbohydrates that have three to ten monomer units.
- Tetra – Four
- Saccharides – Carbohydrates
This breakdown is a big hint and should point you in the right direction towards solving this question.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first analyse what tetrasaccharides really are before moving on to their general formula.
- A tetrasaccharide is defined as a carbohydrate which, upon hydrolysis, results in the formation of four molecules of similar or different monosaccharides. For instance, stachyose upon hydrolysis gives one molecule each of glucose and fructose and two molecules of galactose. However they are in their respective furanose and pyranose form when involved in tetrasaccharide. Its structure is as follows:

Observe the presence of four different monosaccharide structures present in its overall chemical structure. In its hydrolysis, notice that a water molecule has effectively been added across the glycosidic linkages resulting in the formation of four monosaccharides; glucose, fructose and two molecules of galactose.
\[\text{Tetrasaccharide}\xrightarrow{{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}}4\cdot \text{Monosaccharide}\]
The general formula of a tetrasaccharide is ${{C}_{24}}{{H}_{42}}{{O}_{21}}$ .
Another very important example of a tetrasaccharide is Maltotetraose, which is a kind of Maltodextrin which is a polysaccharide (many carbohydrates joined together in a molecular chain) that is used as a food additive which is easily digestible, being absorbed as rapidly as glucose and may be either moderately sweet or almost flavourless.
- In addition to them, Lychnose, Maltotetrose and Sesame are also examples of tetrasaccharides.
Note: We can say that all tetrasaccharides are oligosaccharides, but we cannot say that all oligosaccharides are tetrasaccharides because oligosaccharides involves carbohydrates that have three to ten monomer units.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




